
Plastic pollution is a critical environmental challenge, compelling governments and organizations worldwide to implement stringent measures to curb its management and impact. In Europe, plastic taxation has become a pivotal strategy to reduce plastic waste and promote recycling.
From the European Union (EU) Plastics Levy and Single-Use Plastics (SUP) Directive 2019/904 to Plastic Packaging Waste Regulations and Plastic Packaging Taxes being introduced by member states, Europe’s legislative landscape is nothing short of a maze and presents challenges for enterprises, especially small-scale businesses to stay ahead of the law with the right data and information systems for compliance.
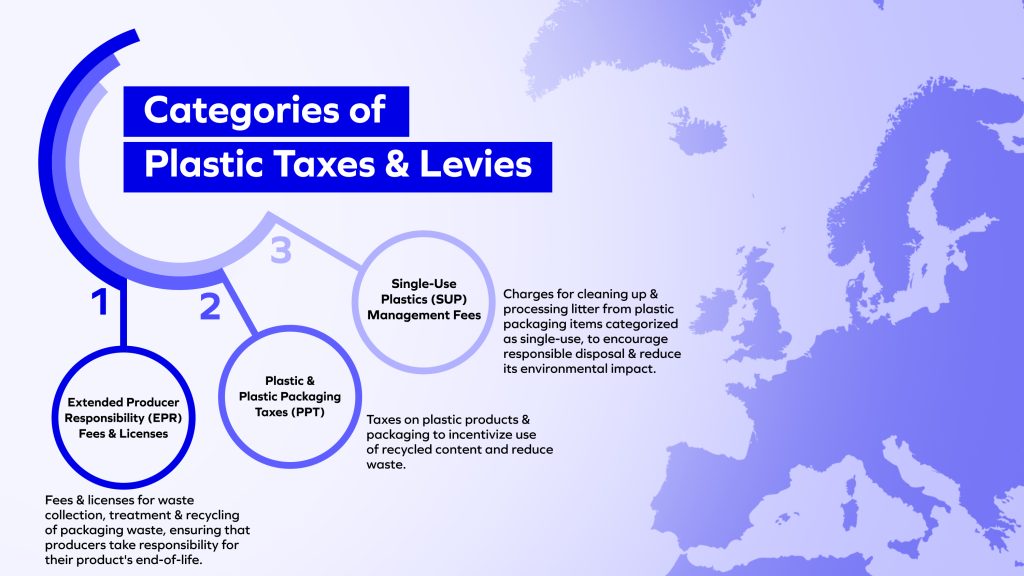
Categories of Plastic Fees, Levies and Taxes
Plastic taxation in Europe can be categorized into 3 main types:
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Fees and Licenses: Fees and licenses for waste collection, treatment and recycling of packaging waste, ensuring that producers take responsibility for their products’ end-of-life.
- Plastic and Plastic Packaging Taxes (PPT): Taxes on plastic products and packaging to incentivize use of recycled content and reduce waste.
- Single-Use Plastics (SUP) Management Fees: Charges for cleaning up and processing litter from plastic packaging items categorized as single-use, to encourage responsible disposal and reduce its environmental impact.
Challenges for Enterprises
Navigating the complex landscape of plastic taxation poses several challenges for businesses:
- Uncoordinated Rules: The lack of harmonization across Member States requires companies to understand and comply with different regulations in each country.
- Identifying Liable Entities: Determining which entity in the supply chain is liable for the tax can be complicated, especially for multinational companies.
- Compliance Requirements: Adapting internal processes, training employees, and maintaining detailed records to meet compliance obligations can be resource-intensive.
- Evolving Regulations: Keeping up with constantly changing requirements demands continuous monitoring and flexibility to adjust compliance strategies.
Experiences in the UK and Spain
United Kingdom: The UK introduced the Plastic Packaging Tax (PPT) on April 1, 2022, targeting plastic packaging with less than 30% recycled content. The tax rate is GBP 200 per tonne of plastic packaging. Businesses must register for the tax, maintain records, and submit quarterly returns. The UK has also implemented a penalty regime for non-compliance, including fines and interest charges. This proactive approach has encouraged companies to increase the use of recycled materials and improve their environmental footprint.
Spain: Spain implemented the Plastic Packaging Tax on January 1, 2023, with a tax rate of EUR 0.45 per kilogram of non-reusable plastic packaging. Similar to the UK, Spanish businesses must register, keep detailed records, and file quarterly returns. The Spanish government has introduced penalties for non-compliance, reinforcing the importance of adhering to the new regulations. The tax has spurred innovations in packaging design and increased the adoption of sustainable materials.
Delays in Germany and Italy
Germany: Germany planned to introduce a national plastic tax in 2025 but has faced delays due to challenges in data collection and concerns over excessive bureaucracy. The German government is working to finalize a practical model for the tax, considering postponing its introduction to 2026. These delays highlight the complexity of implementing new taxation systems and the need for robust infrastructure to support compliance.
Italy: Italy’s Plastic Packaging Tax (PPT) was initially set to take effect in 2024 but has been postponed to January 1, 2026. The delay is attributed to the need for more time to develop an efficient, low-bureaucracy solution and assess the economic impacts. Stakeholder feedback and the potential burden on small and medium-sized enterprises have also influenced the decision to delay the implementation.
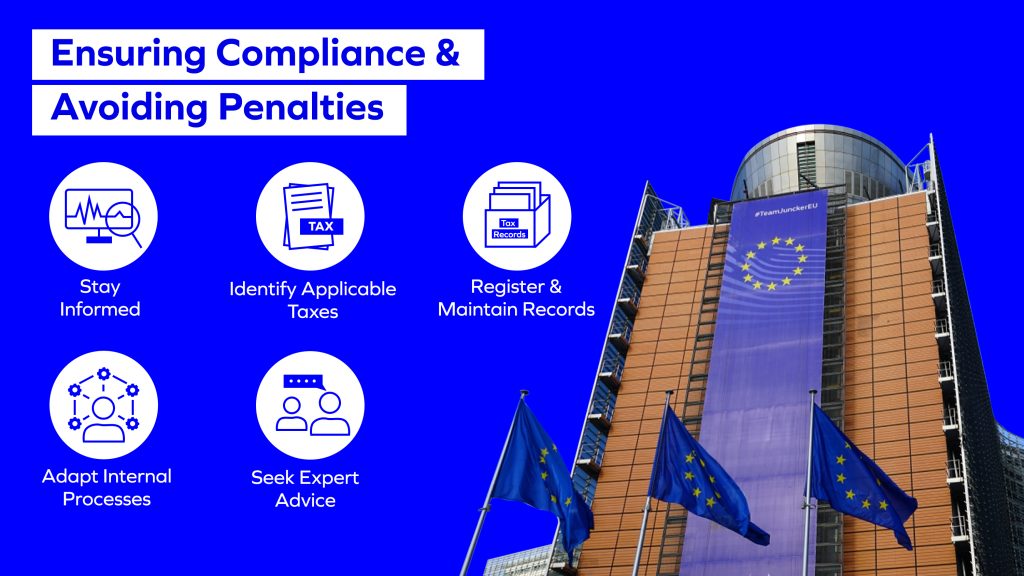
Ensuring Compliance and Avoiding Penalties
Staying ahead of the plastic taxation legislations requires a sound understanding of the interaction between EU level and Member State plastic taxes and EPR compliance. For effective navigation, businesses should adopt proactive strategies:
- Stay Informed: Regularly monitor legislative changes and updates to ensure compliance with the latest regulations.
- Identify Applicable Taxes: Determine which taxes apply to your products and operations in each Member State.
- Register and Maintain Records: Ensure timely registration for applicable taxes, maintain detailed records, and file accurate tax returns.
- Adapt Internal Processes: Implement internal controls, train employees, and establish monitoring and reporting mechanisms
- Seek Expert Advice: Consult with tax and legal experts to develop efficient tax strategies and avoid unnecessary costs.
Plastic taxation in Europe is now a crucial component of the broader strategy to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainability. While it presents challenges for businesses, proactive planning, and compliance strategies can help mitigate risks and ensure adherence to regulations. Navigating the hurricane of laws and regulations is crucial for all connected businesses, all in the best interest of doing good for people and the planet.


Great content, thanks for posting.
Saved as a favorite, I really like your blog!
Do you have a spam issue on this site; I also am a blogger, and I was curious about your situation; we have developed some nice methods and we are looking to exchange strategies with other folks, why not shoot me an email if interested.
новости сегодня
Exodermin y su acción hidratante en la piel afectada
La hidratación es esencial para mantener la belleza de la dermis.
Muchas personas, en su búsqueda por restaurar la vitalidad
de su rostro, descubren opciones innovadoras. En este contexto, hay productos
formulados para brindar ese alivio tan necesario. Pero, ¿realmente funcionan? La
respuesta depende de los componentes que cada uno posee.
La sensación de sequedad puede resultar incómoda y antiestética.
Con el tiempo, la falta de humedad provoca que la superficie se
vea apagada. Además, genera la aparición de líneas
y arrugas. Esto puede ser frustrante y, a menudo, ataca la confianza en uno mismo.
Para aquellos que buscan soluciones, formularios avanzados
prometen resultados visibles. Al combinar ingredientes naturales
y tecnología moderna, se logran efectos sorprendentes.
Aunque parezca un desafío encontrar el producto adecuado, es posible.
La clave está en comprender cómo cada elemento actúa en nuestro organismo.
Uno de los beneficios más destacados de estos exclusivos preparados es su capacidad
para restaurar y reafirmar el tejido, ofreciendo una renovación profunda y notable.
La combinación precisa de elementos activos no solo proporciona
una sensación de frescura, sino que también impulsa la regeneración celular, permitiendo que la superficie luzca
radiante y saludable. Por lo tanto, es fundamental elegir sabiamente y entender cómo funciona
cada componente.
Conocer la manera en que interactúan estos tratamientos con nuestras necesidades es indispensable.
El cuidado apropiado transformará la experiencia diaria.
Con el tiempo, se puede lograr un efecto acumulativo que se traduce en un impacto duradero.
Al final, la satisfacción y el bienestar son lo que realmente buscamos.
Efectividad en la hidratación cutánea
Cuando se trata de mantener la dermis en óptimas condiciones, es esencial
contar con un aliado eficaz. Existen productos que no solo proporcionan una sensación de frescura, sino que también nutren profundamente.
La capacidad de restaurar y revitalizar es fundamental para el bienestar.
Aquí, la innovación juega un papel crucial, permitiendo que la gente disfrute de resultados visibles en poco
tiempo.
Es interesante notar que ciertos compuestos naturales
potencian la humectación de la superficie. Con cada aplicación,
se pueden observar cambios significativos. Esa es una de las claves del éxito:
la fórmula seleccionada. Además, el equilibrio entre la saturación y la pérdida de agua se
convierte en el objetivo primordial, y, por ende, se busca una solución que favorezca ese proceso.
Lo que muchos buscan es un producto que no sea grasoso, que penetre
rápidamente y brinde alivio inmediato. La textura juega un papel importante en esto.
Además, la sensación después de su uso puede ser sorprendentemente placentera,
lo que invita a aplicarlo regularmente. Algunos usuarios han comentado que desde la primera aplicación notaron una diferencia notable, lo que
genera expectativas sobre el uso a largo plazo.
Por lo tanto, la eficacia no radica únicamente en el primer impacto, sino en la capacidad de mantener
la mejora con el tiempo. La combinación de ingredientes
activos permite abordar múltiples problemas que pueden surgir.
Desde la sequedad hasta pequeñas irritaciones, se convierten en parte del pasado
cuando se implementa uno de estos innovadores productos.
Así es como, poco a poco, se establece una rutina que beneficia no
solo la estética sino también la salud dérmica.
Beneficios para la dermis dañada
El uso de ciertos productos puede transformar significativamente la salud de la superficie externa.
Cuando la dermis sufre daños, es fundamental contar con una solución efectiva que ayude a repararla y revitalizarla.
Estos productos tienen la capacidad de nutrir la zona comprometida.
Además, aportan propiedades que facilitan una recuperación más rápida.
Esto se traduce en una apariencia más saludable y radiante.
Uno de los grandes ventajas es su potenciación de la
regeneración celular. La renovación de las células es crucial para restaurar el brillo
natural. El suavizado de las texturas irregulares también se vuelve evidente poco a poco.
A medida que avanzamos en el tratamiento, se nota una disminución del enrojecimiento y la irritación. Esto no solo mejora la estética, sino que también genera confianza en quienes lo utilizan.
Las propiedades que poseen estos productos abarcan una gama amplia de beneficios.
Por ejemplo, forman una barrera que protege de agresores externos.
Esto, a su vez, minimiza la posibilidad de futuras complicaciones.
Con el tiempo, estos compuestos se instalan en la epidermis, ofreciendo
un efecto prolongado. Es como un abrazo reconfortante para la zona comprometida.
Adicionalmente, la sensación de alivio que se
experimenta es inmediata. La hidratación profunda y constante calma cualquier malestar existente.
A través de su aplicación regular, los resultados se van consolidando, convirtiéndose en parte
de la rutina diaria. La satisfacción que brinda cuidar de
uno mismo es incomparable, y el uso adecuado de estos productos lo hace posible.
precio de exodermin
https://rekforum.ru/viewtopic.php?t=46795
fap porno
кракен tor
кракен login
кракен onion
kraken тор браузер
kraken market
kraken mirror
kraken ссылка
кракен
сайт kraken даркнет
kraken зеркало
кракен даркнет маркет
kraken tor
кракен даркнет маркет
kraken даркнет маркет
kraken зайти
кракен рабочее зеркало
kraken обход блокировки
кракен зайти
кракен onion
kraken актуальная ссылка
кракен darknet market
kraken сайт
кракен тор браузер
кракен ссылка
кракен тор браузер
кракен маркет
кракен ссылка tor
kraken даркнет
kraken login
kraken даркнет маркет
кракен вход
kraken даркнет маркет
кракен tor зеркало
kraken актуальная ссылка
кракен link
кракен официальный сайт
kraken официальный сайт
kraken рабочее зеркало
кракен ссылка tor
кракен market
кракен market
kraken
kraken tor зеркало
кракен зеркало
kraken зеркало
kraken onion
кракен сайт
kraken onion
кракен ссылка tor
кракен onion
как зайти на кракен даркнет
kraken рабочее зеркало
kraken официальный сайт
кракен актуальная ссылка
kraken ссылка
кракен market
kraken вход
kraken даркнет маркет
kraken darknet market
кракен зайти
кракен tor зеркало
kraken market
кракен ссылка tor
kraken tor зеркало
kraken darknet tor
кракен mirror
hello there and thanks for your information – I have certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did alternatively expertise some technical points the usage of this website, as I experienced to reload the web site many instances previous to I could get it to load properly. I had been brooding about if your web hosting is OK? No longer that I am complaining, but slow loading instances occasions will sometimes impact your placement in google and can injury your quality score if advertising and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Anyway I’m including this RSS to my e-mail and can glance out for much more of your respective interesting content. Ensure that you update this once more very soon..
Actually, I had to find Zithromax quickly and discovered Antibiotics Express. It allows you to purchase generics online securely. In case of strep throat, this is the best place. Fast shipping to USA. More info: purchase zithromax. Good luck.
Lately, I needed antibiotics urgently and found a reliable pharmacy. They let you get treatment fast safely. If you have a bacterial infection, try here. Express delivery available. Check it out: purchase zithromax. Get well soon.
Lately, I had to buy Amoxicillin for a toothache and came across Amoxicillin Express. They sell effective treatment overnight. If you are in pain, this is the best place: buy amoxicillin online. Cheers.
Bocoran slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Situs ini gampang menang dan resmi. Bonus new member menanti anda. Akses link: п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot login raih kemanangan.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, doğru yerdesiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Xoş gəldin bonusu sizi gözləyir. Keçid: Pin Up giriş qazancınız bol olsun.
2026 yılında en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Detaylı liste platformumuzda mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. Hemen tıklayın https://cassiteleri.us.org/# kaçak bahis siteleri fırsatı kaçırmayın.
Pin Up Casino ölkəmizdə ən populyar kazino saytıdır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki burada baxın.
Pin-Up AZ ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və Aviator var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki Pin Up rəsmi sayt baxın.
Salamlar, siz də yaxşı kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. İndi qoşulun və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Daxil olmaq üçün link: Pin Up uğurlar hər kəsə!
Selamlar, ödeme yapan casino siteleri arıyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye kesinlikle göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve fırsatları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: casino siteleri bol şanslar.
Bocoran slot gacor hari ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Situs ini anti rungkad dan resmi. Bonus new member menanti anda. Kunjungi: п»їslot gacor raih kemanangan.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, doğru yerdesiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və qazanmağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up online uğurlar.
Bu sene en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı web sitemizde mevcuttur. Bedava bahis veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için https://cassiteleri.us.org/# mobil ödeme bahis kazanmaya başlayın.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, bura baxa bilərsiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up kazino hamıya bol şans.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, bura baxa bilərsiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə hesabınıza girin və qazanmağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: Pin Up online uğurlar.
2026 yılında en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı web sitemizde mevcuttur. Bedava bahis veren siteleri ve güncel giriş linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için https://cassiteleri.us.org/# mobil ödeme bahis kazanmaya başlayın.
Selamlar, ödeme yapan casino siteleri arıyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye kesinlikle göz atın. Lisanslı firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Dolandırılmamak için doğru adres: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# listeyi gör bol şanslar.
п»їHalo Slotter, lagi nyari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Pulsa tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot link alternatif semoga maxwin.
Info slot gacor hari ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini anti rungkad dan resmi. Bonus new member menanti anda. Kunjungi: https://bonaslotind.us.com/# bonaslotind.us.com dan menangkan.
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar platformadır. Burada minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Pulu kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up rəsmi sayt baxın.
Halo Bosku, lagi nyari situs slot yang hoki? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Deposit bisa pakai Pulsa tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: situs slot resmi salam jackpot.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# casino siteleri 2026 Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği casino siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: bonus veren siteler Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Onaylı bahis siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# listeyi gör Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Onaylı casino siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
Pin-Up AZ ölkəmizdə ən populyar kazino saytıdır. Burada minlərlə oyun və Aviator var. Qazancı kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki Pin Up AZ baxın.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için kılavuz niteliğinde bir site: bonus veren siteler Hangi site güvenilir diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği bahis siteleri listesi ile rahatça oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Pin-Up AZ Azərbaycanda ən populyar kazino saytıdır. Burada minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Pulu kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt https://pinupaz.jp.net/# pinupaz.jp.net yoxlayın.
HÉ™r vaxtınız xeyir, É™gÉ™r siz etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mÉ™slÉ™hÉ™tdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Æn yaxşı slotlar vÉ™ rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin vÉ™ bonus qazanın. Daxil olmaq üçün link: sayta keçid uÄŸurlar hÉ™r kÉ™sÉ™!
Salam dostlar, siz dÉ™ keyfiyyÉ™tli kazino axtarırsınızsa, mÉ™slÉ™hÉ™tdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Æn yaxşı slotlar vÉ™ rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Ä°ndi qoÅŸulun vÉ™ ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Oynamaq üçün link: sayta keçid uÄŸurlar hÉ™r kÉ™sÉ™!
Bu sene popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı web sitemizde mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için https://cassiteleri.us.org/# mobil ödeme bahis fırsatı kaçırmayın.
2026 yılında en çok kazandıran casino siteleri hangileri? Detaylı liste platformumuzda mevcuttur. Bedava bahis veren siteleri ve güncel giriş linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için casino siteleri 2026 fırsatı kaçırmayın.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, doğru yerdesiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə hesabınıza girin və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up giriş uğurlar.
Info slot gacor malam ini: mainkan Gate of Olympus atau Mahjong Ways di Bonaslot. Website ini gampang menang dan aman. Bonus new member menanti anda. Akses link: п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot raih kemanangan.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# bonus veren siteler Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği bahis siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Tüm liste linkte.
Salam Gacor, cari situs slot yang hoki? Coba main di Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Deposit bisa pakai Pulsa tanpa potongan. Login disini: Bonaslot link alternatif salam jackpot.
Selam, sağlam casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, hazırladığımız listeye mutlaka göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve bonusları sizin için inceledik. Dolandırılmamak için doğru adres: siteyi incele bol şanslar.
Pin-Up AZ ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Burada çoxlu slotlar və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin-Up Casino tövsiyə edirəm.
Salamlar, əgər siz etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Canlı oyunlar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və bonus qazanın. Sayta keçmək üçün link: Pin-Up Casino uğurlar hər kəsə!
Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online nomor 1 di Indonesia. Ribuan member sudah mendapatkan Jackpot sensasional disini. Transaksi super cepat hanya hitungan menit. Link alternatif п»їhttps://bonaslotind.us.com/# bonaslotind.us.com jangan sampai ketinggalan.
Aktual Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, bura baxa bilərsiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: Pin-Up Casino hamıya bol şans.
Halo Slotter, cari situs slot yang gacor? Coba main di Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan pasti bayar. Deposit bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: Bonaslot link alternatif semoga maxwin.
Hər vaxtınız xeyir, əgər siz keyfiyyətli kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. İndi qoşulun və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Oynamaq üçün link: ətraflı məlumat uğurlar hər kəsə!
Pin Up Casino ölkəmizdə ən populyar platformadır. Burada çoxlu slotlar və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza tez köçürürlər. Mobil tətbiqi də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Giriş linki rəsmi sayt tövsiyə edirəm.
Salamlar, siz də etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, məsləhətdir ki, Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və rahat pul çıxarışı burada mövcuddur. İndi qoşulun və bonus qazanın. Daxil olmaq üçün link: Pinup uğurlar hər kəsə!
п»їHalo Bosku, cari situs slot yang gacor? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. Winrate tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai OVO tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: п»їsitus slot resmi salam jackpot.
Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online nomor 1 di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah mendapatkan Jackpot sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat kilat. Situs resmi https://bonaslotind.us.com/# Bonaslot link alternatif jangan sampai ketinggalan.
Canlı casino oynamak isteyenler için rehber niteliğinde bir site: https://cassiteleri.us.org/# türkçe casino siteleri Nerede oynanır diye düşünmeyin. Editörlerimizin seçtiği bahis siteleri listesi ile sorunsuz oynayın. Detaylar linkte.
Situs Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah merasakan Maxwin sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat hanya hitungan menit. Situs resmi Bonaslot link alternatif jangan sampai ketinggalan.
Selamlar, ödeme yapan casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye mutlaka göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: güvenilir casino siteleri iyi kazançlar.
Bonaslot adalah agen judi slot online terpercaya di Indonesia. Banyak member sudah merasakan Jackpot sensasional disini. Proses depo WD super cepat kilat. Situs resmi п»їslot gacor gas sekarang bosku.
Aktual Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtaranlar, bura baxa bilərsiniz. Bloklanmayan link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: https://pinupaz.jp.net/# Pin Up qazancınız bol olsun.
Yeni Pin Up giriş ünvanını axtarırsınızsa, doğru yerdesiniz. İşlək link vasitəsilə qeydiyyat olun və oynamağa başlayın. Pulsuz fırlanmalar sizi gözləyir. Keçid: Pin Up yüklə uğurlar.
Bu sene popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Cevabı platformumuzda mevcuttur. Bedava bahis veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için güvenilir casino siteleri fırsatı kaçırmayın.
Merhaba arkadaşlar, güvenilir casino siteleri arıyorsanız, bu siteye kesinlikle göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve bonusları sizin için inceledik. Güvenli oyun için doğru adres: canlı casino siteleri iyi kazançlar.
Hər vaxtınız xeyir, siz də yaxşı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və sürətli ödənişlər burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Sayta keçmək üçün link: Pinup uğurlar hər kəsə!
Salamlar, siz də etibarlı kazino axtarırsınızsa, mütləq Pin Up saytını yoxlayasınız. Yüksək əmsallar və sürətli ödənişlər burada mövcuddur. Qeydiyyatdan keçin və ilk depozit bonusunu götürün. Oynamaq üçün link: Pin Up uğurlar hər kəsə!
Pin Up Casino ölkəmizdə ən populyar kazino saytıdır. Saytda minlərlə oyun və canlı dilerlər var. Qazancı kartınıza anında köçürürlər. Proqramı də var, telefondan oynamaq çox rahatdır. Rəsmi sayt https://pinupaz.jp.net/# bura daxil olun baxın.
Selamlar, güvenilir casino siteleri bulmak istiyorsanız, bu siteye kesinlikle göz atın. En iyi firmaları ve bonusları sizin için listeledik. Dolandırılmamak için doğru adres: cassiteleri.us.org bol şanslar.
Bu sene popüler olan casino siteleri hangileri? Detaylı liste platformumuzda mevcuttur. Deneme bonusu veren siteleri ve yeni adres linklerini paylaşıyoruz. İncelemek için en iyi casino siteleri kazanmaya başlayın.
Salam Gacor, cari situs slot yang hoki? Rekomendasi kami adalah Bonaslot. RTP Live tertinggi hari ini dan terbukti membayar. Isi saldo bisa pakai Dana tanpa potongan. Daftar sekarang: Bonaslot salam jackpot.
Greetings, I recently discovered an excellent online drugstore for purchasing medications hassle-free. For those who need antibiotics, OnlinePharm is very good. Fast delivery plus huge selection. Check it out: visit website. Cya.
To be honest, I just found a reliable resource to buy medication. If you want to save money and need meds from Mexico, Pharm Mex is highly recommended. No prescription needed plus very reliable. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Good luck!
Hey there, I just came across an awesome Mexican pharmacy to buy medication. If you are tired of high prices and want meds from Mexico, this store is the best option. Great prices and very reliable. Take a look: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Take care.
Hello, To be honest, I found a reliable online drugstore for purchasing generics online. If you need cheap meds, this site is very good. Great prices and huge selection. See for yourself: Online Pharm Store. Cheers.
Hi all, Just now found the best Indian pharmacy to buy generics. If you want to buy medicines from India cheaply, this store is worth checking. You get lowest prices to USA. More info here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Best regards.
Hey there, I wanted to share a reliable international pharmacy for purchasing prescription drugs securely. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, this store is the best choice. Great prices and no script needed. Link here: read more. Thank you.
Greetings, Lately ran into an awesome Mexican pharmacy to save on Rx. If you are tired of high prices and need generic drugs, this site is highly recommended. Great prices plus very reliable. Check it out: cheap antibiotics mexico. Good luck with everything.
Hello, I wanted to share a reliable website where you can buy generics online. If you are looking for antibiotics, this store is highly recommended. Fast delivery and it is very affordable. Check it out: cheap pharmacy online. Thanks!
Hi, To be honest, I found a great source for meds for purchasing generics cheaply. For those who need cheap meds, this store is worth a look. They ship globally plus huge selection. Visit here: check availability. Appreciate it.
Hey there, Lately came across a great Mexican pharmacy for affordable pills. If you are tired of high prices and need cheap antibiotics, Pharm Mex is a game changer. Great prices plus it is safe. Check it out: Pharm Mex. Be well.
Hey there, Just now ran into a reliable Mexican pharmacy to save on Rx. For those seeking and need meds from Mexico, this site is highly recommended. They ship to USA plus secure. Take a look: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Thanks!
Hello everyone, Lately found a great website for cheap meds. For those seeking and need meds from Mexico, this site is a game changer. Fast shipping plus very reliable. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Regards.
Hey there, I wanted to share a useful source for meds where you can buy medications cheaply. If you need no prescription drugs, this site is very good. Fast delivery plus no script needed. Check it out: international pharmacy online. Stay safe.
Hey there, I recently discovered a great online drugstore where you can buy medications cheaply. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Fast delivery and no script needed. Visit here: online pharmacy usa. Thank you.
Hey there, I wanted to share a great website for purchasing medications securely. For those who need no prescription drugs, this site is very good. Fast delivery plus huge selection. See for yourself: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope it helps.
Hello, I just discovered the best Indian pharmacy to save on Rx. For those looking for cheap antibiotics at factory prices, this store is highly recommended. It has fast shipping guaranteed. Take a look: indian pharmacy online. Hope it helps.
Greetings, Lately came across the best Indian pharmacy to save on Rx. If you want to buy medicines from India at factory prices, this site is the best place. It has wholesale rates guaranteed. Check it out: click here. Cheers.
Hello everyone, I recently found a reliable Mexican pharmacy to save on Rx. If you are tired of high prices and need cheap antibiotics, Pharm Mex is a game changer. Great prices and very reliable. Visit here: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Thank you.
Hey there, To be honest, I found a reliable source for meds for purchasing medications cheaply. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, this site is very good. They ship globally plus huge selection. Visit here: Online Pharm Store. Be well.
Greetings, Lately found a great resource to buy medication. If you are tired of high prices and need generic drugs, this store is worth checking out. No prescription needed and secure. Take a look: read more. Best wishes.
Greetings, I wanted to share a great international pharmacy for purchasing medications securely. If you need antibiotics, this store is very good. Secure shipping plus no script needed. Check it out: visit website. Regards.
Hey there, I recently discovered an excellent website for purchasing pills cheaply. For those who need antibiotics, this store is worth a look. They ship globally plus it is very affordable. See for yourself: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Best regards.
Hey guys, Just now discovered a useful website for cheap meds. For those looking for cheap antibiotics at factory prices, this site is worth checking. They offer wholesale rates guaranteed. Check it out: India Pharm Store. Best regards.
Hello, Lately stumbled upon the best source from India for affordable pills. For those looking for cheap antibiotics without prescription, this site is very reliable. They offer secure delivery guaranteed. More info here: order medicines from india. Good luck.
Greetings, Lately found an awesome Mexican pharmacy for affordable pills. For those seeking and want cheap antibiotics, this store is a game changer. They ship to USA plus secure. Visit here: check availability. Hope it helps.
Greetings, I wanted to share a reliable source for meds where you can buy prescription drugs securely. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is very good. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. See for yourself: Online Pharm Store. Kind regards.
Hey everyone, I wanted to share a great source for meds for purchasing generics cheaply. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this store is worth a look. They ship globally and huge selection. Link here: international pharmacy online. Be well.
Hello, I recently discovered a great international pharmacy to order prescription drugs online. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this site is very good. Great prices plus it is very affordable. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Good luck!
Greetings, I just came across a great source from India for cheap meds. If you want to buy generic pills safely, this store is very reliable. You get fast shipping to USA. Check it out: buy meds from india. Cheers.
Hi all, Just now discovered an amazing online drugstore to save on Rx. If you need medicines from India without prescription, IndiaPharm is the best place. It has fast shipping to USA. More info here: India Pharm Store. Good luck.
Hello, To be honest, I found an excellent online drugstore where you can buy medications hassle-free. If you need antibiotics, this store is highly recommended. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. Check it out: online pharmacy no prescription. I hope you find what you need.
Hey there, I just found a reliable online source for affordable pills. If you are tired of high prices and need affordable prescriptions, Pharm Mex is the best option. They ship to USA plus very reliable. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Best wishes.
Hi, I recently discovered an excellent website where you can buy prescription drugs hassle-free. If you are looking for safe pharmacy delivery, this store is highly recommended. They ship globally and it is very affordable. See for yourself: Trust Pharmacy online. Hope it helps.
Greetings, I recently came across the best Indian pharmacy to save on Rx. For those looking for generic pills without prescription, this store is the best place. You get lowest prices guaranteed. More info here: check availability. Cheers.
Hey everyone, I just found a reliable website where you can buy prescription drugs cheaply. For those who need safe pharmacy delivery, this store is the best choice. Great prices plus huge selection. Check it out: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Best regards.
Greetings, I wanted to share a reliable online drugstore where you can buy pills cheaply. If you are looking for cheap meds, this store is the best choice. Secure shipping and it is very affordable. Link here: OnlinePharm. Thank you.
Hello everyone, Lately found a trusted online source for cheap meds. If you want to save money and want affordable prescriptions, this store is the best option. Fast shipping plus very reliable. Link is here: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Best regards.
Greetings, I recently ran into a great website for cheap meds. For those seeking and want generic drugs, Pharm Mex is the best option. They ship to USA and secure. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. Cheers.
To be honest, I just stumbled upon the best website for affordable pills. If you need ED meds without prescription, this site is very reliable. They offer fast shipping worldwide. Take a look: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Hope it helps.
Hi, I just found a reliable source for meds to order pills cheaply. If you are looking for no prescription drugs, OnlinePharm is the best choice. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. Check it out: online pharmacy usa. Best wishes.
Hello, I just found an excellent website to order generics hassle-free. If you need safe pharmacy delivery, OnlinePharm is worth a look. Secure shipping plus it is very affordable. Visit here: https://onlinepharm.jp.net/#. Hope this was useful.
Hi guys, I recently discovered a reliable website for cheap meds. If you want to save money and need affordable prescriptions, Pharm Mex is a game changer. Great prices plus it is safe. Check it out: mexican pharmacy. Thx.
Please let me know if you’re looking for a writer for your site. You have some really good articles and I think I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d love to write some material for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please shoot me an e-mail if interested. Kudos!
To be honest, Just now discovered an awesome online source for affordable pills. If you are tired of high prices and want cheap antibiotics, this site is worth checking out. They ship to USA plus it is safe. Take a look: safe mexican pharmacy. Best regards.
Hey guys, I recently discovered the best Indian pharmacy for affordable pills. If you need generic pills safely, this site is very reliable. You get wholesale rates guaranteed. Take a look: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
Greetings, I recently stumbled upon an amazing Indian pharmacy to buy generics. For those looking for generic pills at factory prices, this site is the best place. You get wholesale rates guaranteed. More info here: India Pharm Store. Best regards.
Hi guys, I just came across an awesome website to save on Rx. If you want to save money and want meds from Mexico, this site is worth checking out. They ship to USA plus it is safe. Check it out: check availability. Best of luck.
Greetings, Just now came across the best online drugstore to save on Rx. If you want to buy cheap antibiotics without prescription, IndiaPharm is worth checking. It has wholesale rates worldwide. More info here: visit website. Cheers.
Hey there, I just discovered a trusted website for cheap meds. If you want to save money and need generic drugs, Pharm Mex is the best option. No prescription needed and very reliable. Visit here: visit website. Best of luck.
code promo melbet du jour telecharger melbet apk
Hey there, I just came across an awesome resource to buy medication. For those seeking and want meds from Mexico, this store is a game changer. They ship to USA and very reliable. Visit here: check availability. Have a great week.
Hello everyone, Just now ran into a reliable online source to save on Rx. If you are tired of high prices and need cheap antibiotics, Pharm Mex is worth checking out. They ship to USA plus very reliable. Check it out: https://pharm.mex.com/#. I hope you find what you need.
application 1win telecharger 1win apk
Hey guys, I recently came across an amazing source from India to buy generics. For those looking for medicines from India cheaply, this store is the best place. You get secure delivery worldwide. Visit here: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Hope it helps.
Hello everyone, I just ran into an awesome Mexican pharmacy for affordable pills. For those seeking and need affordable prescriptions, Pharm Mex is highly recommended. They ship to USA plus it is safe. Take a look: mexican pharmacy online. Hope it helps.
Greetings, Lately stumbled upon a great Indian pharmacy to save on Rx. If you need cheap antibiotics cheaply, this store is worth checking. They offer wholesale rates to USA. Check it out: https://indiapharm.in.net/#. Cheers.
Greetings, I just ran into a great website to save on Rx. For those seeking and need generic drugs, Pharm Mex is worth checking out. Great prices and secure. Take a look: click here. Have a great week.
Matbet güncel linki lazımsa işte burada. Sorunsuz için tıkla: Matbet Yüksek oranlar bu sitede. Gençler, Matbet son linki açıklandı.
Herkese merhaba, Casibom sitesi üyeleri adına önemli bir paylaşım yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi site giriş linkini BTK engeli yüzünden sürekli güncelledi. Giriş sorunu yaşıyorsanız link aşağıda. Resmi siteye erişim bağlantısı şu an aşağıdadır https://casibom.mex.com/# Paylaştığım bağlantı üzerinden doğrudan hesabınıza bağlanabilirsiniz. Ayrıca yeni üyelere verilen yatırım bonusu kampanyalarını da kaçırmayın. En iyi bahis deneyimi sürdürmek için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol şans dilerim.
Arkadaslar, Grandpashabet son linki belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar buradan giris yapabilir https://grandpashabet.in.net/#
Gençler, Grandpashabet Casino son linki açıklandı. Giremeyenler buradan giriş yapabilir Grandpashabet Twitter
Arkadaslar, Grandpashabet yeni adresi belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar su linkten devam edebilir Grandpashabet Guncel
Grandpasha giriş linki arıyorsanız işte burada. Hızlı giriş yapmak için Grandpashabet 2026 Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Arkadaslar selam, Vay Casino kullan?c?lar? icin k?sa bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Bildiginiz gibi site adresini tekrar degistirdi. Giris hatas? varsa panik yapmay?n. Guncel Vay Casino giris adresi su an burada: Vaycasino Yeni Adres Paylast?g?m baglant? uzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye girebilirsiniz. Lisansl? bahis keyfi icin Vaycasino dogru adres. Herkese bol kazanclar dilerim.
Grandpasha guncel adresi laz?msa iste burada. H?zl? giris yapmak icin t?kla https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yuksek oranlar burada.
Нужен проектор? projector24 большой выбор моделей для дома, офиса и бизнеса. Проекторы для кино, презентаций и обучения, официальная гарантия, консультации специалистов, гарантия качества и удобные условия покупки.
Herkese selam, Vaycasino kullanıcıları için önemli bir duyuru paylaşıyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi site giriş linkini yine değiştirdi. Giriş hatası yaşıyorsanız endişe etmeyin. Yeni Vay Casino giriş adresi şu an aşağıdadır: Resmi Site Bu link üzerinden vpn kullanmadan siteye erişebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis deneyimi için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazançlar dilerim.
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler şu linkten giriş yapabilir Grandpashabet İndir
Dostlar selam, Casibom sitesi kullan?c?lar? ad?na onemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Bildiginiz gibi site giris linkini erisim k?s?tlamas? nedeniyle surekli degistirdi. Erisim sorunu varsa cozum burada. Cal?san siteye erisim baglant?s? su an asag?dad?r https://casibom.mex.com/# Paylast?g?m baglant? ile dogrudan siteye erisebilirsiniz. Ek olarak yeni uyelere sunulan freespin f?rsatlar?n? da kac?rmay?n. Lisansl? slot deneyimi icin Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Tum forum uyelerine bol kazanclar dilerim.
Grandpasha giris adresi laz?msa dogru yerdesiniz. H?zl? erisim icin Giris Yap Deneme bonusu bu sitede.
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet son linki belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar şu linkten giriş yapabilir Grandpashabet Giriş
Grandpasha guncel linki ar?yorsan?z iste burada. Sorunsuz erisim icin t?kla https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yuksek oranlar bu sitede.
Arkadaşlar, Grandpashabet son linki açıklandı. Adresi bulamayanlar buradan giriş yapabilir https://grandpashabet.in.net/#
Bahis severler selam, Casibom oyuncular? icin onemli bir bilgilendirme paylas?yorum. Bildiginiz gibi site adresini BTK engeli yuzunden yine guncelledi. Giris hatas? varsa cozum burada. Cal?san Casibom giris baglant?s? su an asag?dad?r Giris Yap Paylast?g?m baglant? uzerinden dogrudan hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Ayr?ca yeni uyelere sunulan yat?r?m bonusu f?rsatlar?n? mutlaka kac?rmay?n. En iyi slot keyfi surdurmek icin Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Herkese bol kazanclar dilerim.
Herkese selam, bu populer site oyuncular? icin onemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Herkesin bildigi uzere site giris linkini erisim k?s?tlamas? nedeniyle yine tas?d?. Giris problemi varsa cozum burada. Son siteye erisim linki art?k asag?dad?r https://casibom.mex.com/# Bu link uzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesab?n?za baglanabilirsiniz. Ayr?ca yeni uyelere verilen yat?r?m bonusu kampanyalar?n? da kac?rmay?n. En iyi slot deneyimi icin Casibom dogru adres. Herkese bol kazanclar dilerim.
Herkese selam, Casibom sitesi üyeleri adına önemli bir duyuru yapmak istiyorum. Bildiğiniz gibi bahis platformu giriş linkini erişim kısıtlaması nedeniyle yine taşıdı. Erişim problemi varsa çözüm burada. Son Casibom giriş adresi şu an burada https://casibom.mex.com/# Bu link ile vpn kullanmadan hesabınıza bağlanabilirsiniz. Ayrıca kayıt olanlara sunulan hoşgeldin bonusu kampanyalarını da kaçırmayın. Güvenilir casino keyfi sürdürmek için Casibom tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol şans dilerim.
Arkadaslar, Grandpashabet Casino son linki belli oldu. Giremeyenler su linkten giris yapabilir Grandpashabet Apk
Arkadaşlar selam, Vay Casino kullanıcıları için önemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Malum platform giriş linkini yine güncelledi. Erişim sorunu yaşıyorsanız endişe etmeyin. Yeni Vaycasino giriş linki şu an burada: Vaycasino Bonus Bu link ile vpn kullanmadan siteye girebilirsiniz. Güvenilir bahis deneyimi sürdürmek için Vaycasino tercih edebilirsiniz. Tüm forum üyelerine bol kazançlar dilerim.
Arkadaslar, Grandpashabet yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler buradan devam edebilir Grandpashabet 2026
Gencler, Grandpashabet yeni adresi belli oldu. Adresi bulamayanlar su linkten devam edebilir https://grandpashabet.in.net/#
Gençler, Grandpashabet Casino yeni adresi belli oldu. Giremeyenler buradan devam edebilir Grandpashabet Kayıt
Grandpasha giris adresi ar?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Sorunsuz giris yapmak icin Grandpashabet Twitter Yuksek oranlar bu sitede.
Grandpashabet giriş adresi arıyorsanız işte burada. Hızlı erişim için https://grandpashabet.in.net/# Yüksek oranlar burada.
Herkese selam, Vaycasino oyuncular? ad?na onemli bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Malum platform giris linkini tekrar degistirdi. Giris hatas? varsa panik yapmay?n. Yeni Vay Casino giris linki su an burada: Vaycasino Twitter Paylast?g?m baglant? ile direkt hesab?n?za erisebilirsiniz. Guvenilir bahis deneyimi icin Vaycasino dogru adres. Herkese bol sans temenni ederim.
Matbet güncel adresi lazımsa işte burada. Sorunsuz için: Matbet Üyelik Yüksek oranlar bu sitede. Arkadaşlar, Matbet son linki açıklandı.
Arkadaslar selam, Vay Casino oyuncular? ad?na k?sa bir bilgilendirme paylas?yorum. Bildiginiz gibi Vaycasino giris linkini tekrar degistirdi. Erisim hatas? varsa panik yapmay?n. Cal?san Vay Casino giris linki su an burada: Resmi Site Bu link ile vpn kullanmadan hesab?n?za erisebilirsiniz. Guvenilir bahis keyfi icin Vay Casino dogru adres. Herkese bol sans temenni ederim.
ремонт и химчистка обуви химчистка обуви в москве
Dostlar selam, Casibom sitesi kullan?c?lar? ad?na k?sa bir bilgilendirme yapmak istiyorum. Bildiginiz gibi Casibom giris linkini erisim k?s?tlamas? nedeniyle tekrar guncelledi. Erisim sorunu yas?yorsan?z dogru yerdesiniz. Guncel Casibom giris linki art?k asag?dad?r https://casibom.mex.com/# Paylast?g?m baglant? ile direkt hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Ayr?ca yeni uyelere sunulan hosgeldin bonusu f?rsatlar?n? mutlaka kac?rmay?n. Guvenilir slot keyfi surdurmek icin Casibom dogru adres. Tum forum uyelerine bol kazanclar dilerim.
Herkese merhaba, Casibom oyuncular? icin k?sa bir paylas?m paylas?yorum. Bildiginiz gibi bahis platformu adresini erisim k?s?tlamas? nedeniyle surekli degistirdi. Giris problemi cekenler icin link asag?da. Cal?san Casibom guncel giris baglant?s? art?k asag?dad?r Casibom Paylast?g?m baglant? uzerinden vpn kullanmadan hesab?n?za girebilirsiniz. Ayr?ca yeni uyelere verilen yat?r?m bonusu kampanyalar?n? da kac?rmay?n. Guvenilir casino deneyimi icin Casibom dogru adres. Tum forum uyelerine bol sans dilerim.
Xin chao 500 anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n ch? n?p rut nhanh d? gi?i tri Da Ga thi tham kh?o trang nay nhe. Dang co khuy?n mai: Nha cai BJ88. Hup l?c d?y nha.
недорогой мужской костюм купить мужской костюм
Chao anh em, ai dang tim c?ng game khong b? ch?n d? gi?i tri N? Hu thi xem th? con hang nay. T?c d? ban th?: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chuc cac bac r?c r?.
Hello m?i ngu?i, ngu?i anh em nao c?n trang choi xanh chin d? choi Da Ga thi vao ngay con hang nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: Nha cai Dola789. Chuc cac bac r?c r?.
Chào anh em, nếu anh em đang kiếm sân chơi đẳng cấp để giải trí Casino thì xem thử địa chỉ này. Không lo lừa đảo: sun win. Về bờ thành công.
Xin chao 500 anh em, ngu?i anh em nao c?n ch? n?p rut nhanh d? g? g?c Game bai thi tham kh?o con hang nay. Khong lo l?a d?o: BJ88. V? b? thanh cong.
Hello mọi người, bác nào muốn tìm trang chơi xanh chín để cày cuốc Casino đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Không lo lừa đảo: https://gramodayalawcollege.org.in/#. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Chào cả nhà, bác nào muốn tìm sân chơi đẳng cấp để gỡ gạc Tài Xỉu thì xem thử trang này nhé. Đang có khuyến mãi: Dola789. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Лучшее казино https://t.me/ играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.
Играешь в казино? апх Слоты, рулетка, покер и live-дилеры, простой интерфейс, стабильная работа сайта и возможность играть онлайн без сложных настроек.
Chào cả nhà, bác nào muốn tìm cổng game không bị chặn để cày cuốc Nổ Hũ đừng bỏ qua con hàng này. Uy tín luôn: Tải app Dola789. Chúc các bác rực rỡ.
Chao anh em, ai dang tim ch? n?p rut nhanh d? cay cu?c N? Hu thi vao ngay trang nay nhe. Khong lo l?a d?o: Link khong b? ch?n. V? b? thanh cong.
Лучшее казино ап икс официальный играйте в слоты и live-казино без лишних сложностей. Простой вход, удобный интерфейс, стабильная платформа и широкий выбор игр для отдыха и развлечения.
Iver Protocols Guide: Iver Protocols Guide – Iver Protocols Guide
Amitriptyline Elavil Generic Elavil
Follicle Insight: generic propecia without prescription – Follicle Insight
AmiTrip Relief Store: AmiTrip Relief Store – AmiTrip
stromectol 3 mg dosage stromectol 3 mg dosage Iver Protocols Guide
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# can i get clomid without prescription
can i get clomid no prescription: fertility pct guide – where can i buy clomid without a prescription
generic propecia price: Follicle Insight – buy propecia without dr prescription
https://amitrip.us.com/# Generic Elavil
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
buying propecia online: get generic propecia pills – cheap propecia without insurance
https://amitrip.us.com/# AmiTrip
Iver Protocols Guide: can you buy stromectol over the counter – Iver Protocols Guide
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# can i get clomid prices
fertility pct guide fertility pct guide fertility pct guide
Elavil: Generic Elavil – AmiTrip Relief Store
Iver Protocols Guide: ivermectin cost – Iver Protocols Guide
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
https://follicle.us.com/# cost cheap propecia tablets
where can i get cheap clomid pills: cost of clomid without a prescription – where buy cheap clomid without prescription
Iver Protocols Guide: ivermectin 500mg – ivermectin 500ml
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# how to buy cheap clomid online
Elavil buy Elavil Elavil
cheap propecia pills: Follicle Insight – buying generic propecia tablets
https://amitrip.us.com/# Elavil
where to buy clomid online: fertility pct guide – can i buy cheap clomid
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# buying generic clomid without dr prescription
where buy cheap clomid without prescription: how to buy clomid without rx – fertility pct guide
fertility pct guide: fertility pct guide – can i buy clomid prices
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# cost of cheap clomid tablets
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
ivermectin nz: ivermectin lotion cost – ivermectin cream
Elavil Generic Elavil Amitriptyline
cost cheap propecia without a prescription: order cheap propecia without a prescription – Follicle Insight
https://iver.us.com/# Iver Protocols Guide
how cЙ‘n i get cheap propecia pills: Follicle Insight – generic propecia
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# fertility pct guide
cost cheap propecia without prescription: Follicle Insight – Follicle Insight
AmiTrip: AmiTrip – Generic Elavil
https://iver.us.com/# ivermectin where to buy
cost cheap propecia price Follicle Insight Follicle Insight
fertility pct guide: fertility pct guide – fertility pct guide
https://follicle.us.com/# Follicle Insight
buy ivermectin cream: Iver Protocols Guide – ivermectin 1 cream 45gm
https://fertilitypctguide.us.com/# can i order generic clomid pill
ivermectin buy australia: Iver Protocols Guide – ivermectin nz
Hello, I recently found dosage instructions regarding prescription drugs, I recommend this drug database. You can read about drug interactions in detail. Read more here: https://magmaxhealth.com/Toradol. Very informative.
Greetings, for those searching for dosage instructions regarding common medicines, I found this useful resource. It explains usage and risks clearly. See details: https://magmaxhealth.com/Clomid. Thanks.
Hello, anyone searching for a trusted online pharmacy to buy prescription drugs online. Check out this pharmacy: lamictal. Selling generic tablets with fast shipping. Hope this helps.
regarding the proper usage instructions, it is recommended to check the official information page at: https://magmaxhealth.com/naltrexone.html which covers safe treatment.
Greetings, if you are looking for dosage instructions regarding health treatments, check out this medical reference. You can read about drug interactions in detail. Link: https://magmaxhealth.com/Rosuvastatin. Very informative.
To start saving, I recommend this reliable site here for the best prices. Get your meds today and save big.
Hey everyone, I recently found a useful article regarding health treatments, I recommend this useful resource. It explains usage and risks in detail. Reference: https://magmaxhealth.com/Naltrexone. Thanks.
Hello, if you need a trusted drugstore to buy medicines online. Check out this site: clomid. Stocking generic tablets and huge discounts. Hope this helps.
To start saving, visit this service pharmacy online usa to order now. Take control of your health and save big.
Hi, if anyone needs dosage instructions on health treatments, take a look at this drug database. You can read about drug interactions in detail. Source: https://magmaxhealth.com/Toradol. Hope this is useful.
To understand the medical specifications, you can consult this resource: https://magmaxhealth.com/rosuvastatin.html for correct administration.
Hey everyone, I wanted to share a great health store to order pills online. I recommend this site: olanzapine. Selling a wide range of meds at the best prices. Best regards.
In terms of side effects and interactions, data is available at the medical directory at: https://magmaxhealth.com/prilosec.html which covers safe treatment.
Greetings, if anyone needs a useful article on common medicines, take a look at this useful resource. You can read about usage and risks very well. Reference: https://magmaxhealth.com/Allopurinol. Good info.
Hi all, for those searching for a useful article about prescription drugs, take a look at this medical reference. You can read about usage and risks very well. Source: https://magmaxhealth.com/Toradol. Thanks.
Hello, if you need a great drugstore to buy medicines online. Check out this pharmacy: toradol. Selling a wide range of meds and huge discounts. Good luck.
For a complete overview of medical specifications, please review this resource: https://magmaxhealth.com/methotrexate.html which covers safe treatment.
Hi all, for those searching for side effects info regarding various medications, take a look at this drug database. It explains how to take meds clearly. Read more here: https://magmaxhealth.com/Allopurinol. Thanks.
Hey everyone, if anyone needs side effects info about various medications, take a look at this useful resource. It covers usage and risks clearly. Link: https://magmaxhealth.com/Methotrexate. Good info.
Hi all, if anyone needs a medical guide on common medicines, I found this useful resource. You can read about how to take meds in detail. Reference: https://magmaxhealth.com/Prilosec. Good info.
regarding the medical specifications, you can consult this resource: https://magmaxhealth.com/lipitor.html for clinical details.
Hello, if you are looking for an affordable health store to purchase pills online. Take a look at MagMaxHealth: toradol. Stocking generic tablets and huge discounts. Good luck.
Nausea Care US: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
Gastro Health Monitor: omeprazole brand name – omeprazole generic
https://gastrohealthmonitor.com/# Gastro Health Monitor
Nausea Care US: Nausea Care US – ondansetron
generic for zofran: buy zofran – ondansetron otc
buy zofran online: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
http://spasmreliefprotocols.com/# methocarbamol robaxin
generic for zofran: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
ondansetron zofran: zofran dosage – Nausea Care US
Nausea Care US Nausea Care US zofran otc
muscle relaxant drugs: Spasm Relief Protocols – muscle relaxers over the counter
tizanidine hcl: robaxin – tizanidine muscle relaxer
https://gastrohealthmonitor.shop/# omeprazole generic
Gastro Health Monitor: omeprazole generic – Gastro Health Monitor
Gastro Health Monitor: Gastro Health Monitor – Gastro Health Monitor
muscle relaxant drugs: Spasm Relief Protocols – п»їbest muscle relaxer
robaxin: over the counter muscle relaxers that work – muscle relaxer tizanidine
prilosec medication: prilosec dosage – omeprazole brand name
https://nauseacareus.com/# ondansetron medication
Gastro Health Monitor: prilosec dosage – prilosec dosage
buy zofran: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
п»їbest muscle relaxer: Spasm Relief Protocols – zanaflex medication
best muscle relaxer: Spasm Relief Protocols – buy tizanidine without prescription
https://nauseacareus.shop/# Nausea Care US
Nausea Care US: Nausea Care US – Nausea Care US
muscle relaxant drugs: buy methocarbamol – buy tizanidine without prescription
Gastro Health Monitor: omeprazole prilosec – Gastro Health Monitor
buy zofran: Nausea Care US – generic for zofran
https://gastrohealthmonitor.shop/# Gastro Health Monitor
Gastro Health Monitor: Gastro Health Monitor – Gastro Health Monitor
Gastro Health Monitor: buy prilosec online – generic prilosec
tizanidine hydrochloride: Spasm Relief Protocols – buy methocarbamol without prescription
https://spasmreliefprotocols.shop/# buy methocarbamol
omeprazole over the counter: prilosec medication – prilosec dosage
muscle relaxers over the counter: tizanidine zanaflex – tizanidine hcl
over the counter muscle relaxers that work: Spasm Relief Protocols – tizanidine generic
Gastro Health Monitor: prilosec generic – Gastro Health Monitor
https://nauseacareus.shop/# ondestranon zofran
robaxin medication: buy tizanidine without prescription – muscle relaxer medication
muscle relaxers over the counter: Spasm Relief Protocols – buy methocarbamol without prescription
https://gastrohealthmonitor.com/# omeprazole over the counter
prilosec side effects: Gastro Health Monitor – prilosec generic
https://gastrohealthmonitor.shop/# omeprazole medication
otc muscle relaxer: Spasm Relief Protocols – antispasmodic medication
http://gastrohealthmonitor.com/# buy prilosec
Nausea Care US: Nausea Care US – zofran over the counter
https://gastrohealthmonitor.shop/# Gastro Health Monitor
http://spasmreliefprotocols.com/# robaxin medication
https://spasmreliefprotocols.shop/# robaxin
robaxin generic: buy tizanidine without prescription – tizanidine hydrochloride
https://nauseacareus.com/# Nausea Care US
top online pharmacy india: online shopping pharmacy india – best online pharmacy india
https://indogenericexport.com/# best india pharmacy
https://indogenericexport.com/# buy methocarbamol without prescription
tizanidine muscle relaxer: Spasm Relief Protocols – otc muscle relaxer
US Meds Outlet: pharmacy online 365 discount code – US Meds Outlet
https://usmedsoutlet.shop/# US Meds Outlet
https://indogenericexport.com/# online shopping pharmacy india
US Meds Outlet: US Meds Outlet – US Meds Outlet
https://indogenericexport.com/# over the counter muscle relaxers that work
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# online pharmacy india
https://bajameddirect.shop/# pharma mexicana
BajaMed Direct: BajaMed Direct – purple pharmacy mexico
https://indogenericexport.shop/# antispasmodic medication
mexican pharmacy menu: BajaMed Direct – mexican pharma
http://indogenericexport.com/# muscle relaxer tizanidine
http://indogenericexport.com/# methocarbamol robaxin
US Meds Outlet: online pharmacy group – canadian pharmacy ltd
humana online pharmacy: US Meds Outlet – escrow pharmacy canada
https://indogenericexport.com/# robaxin medication
medication in mexico: BajaMed Direct – online mexican pharmacy
http://usmedsoutlet.com/# US Meds Outlet
online pharmacy india: п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india – top 10 pharmacies in india
pharmacy website india: Indo-Generic Export – legitimate online pharmacies india
https://indogenericexport.shop/# buy methocarbamol
BajaMed Direct: BajaMed Direct – BajaMed Direct
mexico farmacia: mexico prescriptions – BajaMed Direct
US Meds Outlet: US Meds Outlet – US Meds Outlet
indian pharmacy paypal: top online pharmacy india – best india pharmacy
safe canadian pharmacy: canadian discount pharmacy – US Meds Outlet
mail order pharmacy india: indian pharmacy online – buy prescription drugs from india
reputable indian online pharmacy: world pharmacy india – indianpharmacy com
costco online pharmacy: walgreens online pharmacy – US Meds Outlet
https://usmedsoutlet.com/# no prescription pharmacy paypal
BajaMed Direct: BajaMed Direct – online pharmacies
https://bajameddirect.com/# BajaMed Direct
BajaMed Direct: BajaMed Direct – BajaMed Direct
BajaMed Direct: online pharmacies – farmacia pharmacy mexico
https://indogenericexport.com/# top 10 pharmacies in india
india pharmacy mail order: Indo-Generic Export – india pharmacy
https://bajameddirect.com/# mexican pharmacy
canadian pharmacy 365: pharmacy no prescription required – US Meds Outlet
india pharmacy mail order: Indo-Generic Export – top 10 online pharmacy in india
https://indogenericexport.com/# mail order pharmacy india
online pharmacy india: online pharmacy india – pharmacy website india
Essayez le meilleur nouveau casino en ligne France Bonus de
bienvenue large choix de jeux depots securises et retraits rapides Inscrivez vous des maintenant
I dugg some of you post as I cogitated they were very helpful extremely helpful
uk pharmacy no prescription: US Meds Outlet – US Meds Outlet
http://bajameddirect.com/# phentermine in mexico pharmacy
BajaMed Direct: BajaMed Direct – BajaMed Direct
https://bajameddirect.shop/# BajaMed Direct
online shopping pharmacy india: Indo-Generic Export – world pharmacy india
cheapest online pharmacy india: indian pharmacies safe – top online pharmacy india
https://indogenericexport.shop/# indianpharmacy com
canadian pharmacy generic cialis: canadian online pharmacy viagra – US Meds Outlet
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – generic neurontin pill
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
order zoloft: zoloft without dr prescription – generic for zoloft
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# stromectol tablets buy online
sertraline generic: zoloft without dr prescription – zoloft tablet
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# neurontin 500 mg
stromectol ireland: ivermectin new zealand – ivermectin cost canada
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# good pill pharmacy
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# cost of ivermectin 1% cream
Smart GenRx USA: canadian pharmacy phone number – canadian pharmacy no scripts
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# online pharmacy indonesia
online pharmacy 365: online pharmacy europe – all med pharmacy
Neuro Relief USA Neuro Relief USA Neuro Relief USA
http://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft buy
Neuro Relief USA: neurontin prescription medication – neurontin 300 mg price in india
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – gabapentin generic
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
ivermectin 6mg dosage: ivermectin stromectol – Iver Therapeutics
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# stromectol ireland
Smart GenRx USA Smart GenRx USA Smart GenRx USA
generic for zoloft: sertraline zoloft – zoloft without dr prescription
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# reliable canadian pharmacy reviews
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
http://sertralineusa.com/# sertraline zoloft
Neuro Relief USA neurontin 500 mg tablet Neuro Relief USA
ivermectin 400 mg brands: ivermectin 2mg – ivermectin uk
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# neurontin singapore
stromectol tab price: ivermectin 250ml – Iver Therapeutics
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
order zoloft: order zoloft – zoloft without dr prescription
zoloft without dr prescription order zoloft zoloft generic
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin usa
neurontin 200 mg capsules: gabapentin generic – neurontin medication
Ontvang de beste casino bonussen van 2025!
Speel in legale Nederlandse online casinos, profiteer van free
spins en stortingsbonussen en maak kans op echte geldprijzen. Veilig, snel en eerlijk gokken voor elke speler.
Smart GenRx USA: canadianpharmacyworld – Smart GenRx USA
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft tablet
ivermectin 400 mg brands Iver Therapeutics ivermectin for sale
zoloft pill: zoloft pill – sertraline zoloft
http://sertralineusa.com/# sertraline zoloft
Neuro Relief USA: can i buy neurontin over the counter – neurontin 600 mg coupon
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# canada neurontin 100mg lowest price
generic zoloft: generic zoloft – zoloft without rx
pharmacy express Smart GenRx USA Smart GenRx USA
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# neurontin 4 mg
zoloft cheap: zoloft cheap – buy zoloft
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft generic
top 10 pharmacy websites: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
Neuro Relief USA Neuro Relief USA Neuro Relief USA
best online foreign pharmacies: top online pharmacy 247 – canadien pharmacies
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# Iver Therapeutics
Smart GenRx USA: northern pharmacy canada – Smart GenRx USA
Ce guide est destine aux joueurs qui recherchent une evaluation structuree du
casino en ligne MyStake un site multifonctionnel qui propose un casino des mini jeux des
paris et differents bonus
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
canadian pharmacy online ship to usa: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
sertraline Sertraline USA zoloft generic
buy zoloft: sertraline zoloft – generic zoloft
zoloft without dr prescription: generic zoloft – sertraline zoloft
https://smartgenrxusa.shop/# pharmacy shop
Iver Therapeutics: stromectol drug – stromectol oral
zoloft generic Sertraline USA generic zoloft
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
how much is generic neurontin: neurontin drug – Neuro Relief USA
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft tablet
https://sertralineusa.com/# buy zoloft
canadian pharmacy levitra: pharmaceuticals online australia – Smart GenRx USA
canadian pharmacy world canadian valley pharmacy Smart GenRx USA
Smart GenRx USA: canadian pharmacy king reviews – Smart GenRx USA
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# Iver Therapeutics
sertraline: generic zoloft – zoloft no prescription
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft without dr prescription
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# generic neurontin 300 mg
Neuro Relief USA: buy gabapentin – neurontin 400 mg capsule
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin
ivermectin over the counter ivermectin 3 mg tablet dosage Iver Therapeutics
buy zoloft: buy zoloft – sertraline zoloft
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
canadian pharmacy no prescription: Smart GenRx USA – pharmacy online 365
https://sertralineusa.com/# generic for zoloft
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – buy ivermectin cream
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft without dr prescription
Iver Therapeutics ivermectin lotion for lice Iver Therapeutics
zoloft without rx: zoloft tablet – zoloft cheap
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
ivermectin 12 mg: Iver Therapeutics – ivermectin price comparison
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# rx pharmacy
https://smartgenrxusa.shop/# pharmacy online australia free shipping
neurontin 4 mg: neurontin 100 mg cost – Neuro Relief USA
neurontin discount: Neuro Relief USA – buy neurontin 300 mg
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin 6 mg tablets
buy zoloft zoloft medication zoloft buy
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – neurontin 600 mg price
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# Neuro Relief USA
can i buy neurontin over the counter: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – online pharmacy europe
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# canadian pharmacy without prescription
order zoloft: buy zoloft – zoloft no prescription
neurontin 500 mg: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
Neuro Relief USA gabapentin 600 mg Neuro Relief USA
https://sertralineusa.shop/# generic zoloft
https://smartgenrxusa.shop/# online pharmacy prescription
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – stromectol 3 mg
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# no rx pharmacy
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
Iver Therapeutics Iver Therapeutics Iver Therapeutics
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – medication neurontin 300 mg
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# neurontin 200 mg tablets
ivermectin for sale: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
generic zoloft: Sertraline USA – zoloft cheap
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – neurontin 300mg tablet cost
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
Iver Therapeutics Iver Therapeutics stromectol ivermectin buy
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# Iver Therapeutics
neurontin 800 mg cost: neurontin 300 mg cost – neurontin 500 mg
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – ivermectin 6mg
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – ivermectin 3mg tablets
stromectol tablets uk: stromectol covid – Iver Therapeutics
zoloft without rx sertraline zoloft buy zoloft
http://sertralineusa.com/# sertraline
stromectol medicine: Iver Therapeutics – ivermectin 6mg dosage
Neuro Relief USA: neurontin 800 mg cost – Neuro Relief USA
ремонт дизайн интерьера студия дизайна интерьера спб
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# stromectol cost
Iver Therapeutics: ivermectin oral solution – ivermectin lice
neurontin prescription: neurontin from canada – neurontin brand name 800 mg
http://sertralineusa.com/# generic for zoloft
canadian pharmacy no prescription needed: canadian 24 hour pharmacy – Smart GenRx USA
zoloft generic sertraline zoloft zoloft no prescription
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# Neuro Relief USA
zoloft no prescription: zoloft no prescription – zoloft medication
Neuro Relief USA: neurontin 100 mg cost – neurontin rx
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# neurontin 204
Smart GenRx USA: 24 hours pharmacy – Smart GenRx USA
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# buy ivermectin pills
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – neurontin 900 mg
ivermectin 3mg tablets Iver Therapeutics stromectol how much it cost
professional pharmacy: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# ivermectin usa
https://sertralineusa.shop/# zoloft no prescription
canada pharmacy world: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
stromectol 12mg: ivermectin stromectol – Iver Therapeutics
https://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin 3mg tablets
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – tops pharmacy
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# Iver Therapeutics
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
ivermectin 5 mg ivermectin canada Iver Therapeutics
https://sertralineusa.shop/# order zoloft
http://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft tablet
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# canadapharmacyonline
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – Iver Therapeutics
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – buying from canadian pharmacies
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin over the counter canada
gold pharmacy online Smart GenRx USA Smart GenRx USA
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – cialis canadian pharmacy
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
http://sertralineusa.com/# sertraline
Iver Therapeutics: Iver Therapeutics – stromectol 3mg cost
stromectol cost: Iver Therapeutics – stromectol generic name
https://smartgenrxusa.shop/# Smart GenRx USA
online pharmacy weight loss: Smart GenRx USA – canadian discount pharmacy
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# ivermectin drug
legal online pharmacy coupon code: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
neurontin 50mg cost Neuro Relief USA prescription price for neurontin
Охраны труда для бизнеса охрана труда аудит системы безопасности, обучение персонала, разработка локальных актов и внедрение стандартов. Помогаем минимизировать риски и избежать штрафов.
Проблемы с зубами? стоматологический центр профилактика, лечение, протезирование и эстетическая стоматология. Забота о здоровье зубов с применением передовых методик.
A professional house renovation company Moraira can transform an outdated property into a modern luxury villa. As a leading renovation company Moraira, we bring expert craftsmanship to modernize your kitchen or living areas, significantly increasing your home’s market value.
neurontin 50mg cost: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
A professional house renovation company Moraira can transform an outdated property into a modern luxury villa. As a leading renovation company Moraira, we bring expert craftsmanship to modernize your kitchen or living areas, significantly increasing your home’s market value.
Охраны труда для бизнеса охрана труда дистанционно аудит системы безопасности, обучение персонала, разработка локальных актов и внедрение стандартов. Помогаем минимизировать риски и избежать штрафов.
https://sertralineusa.com/# Sertraline USA
Нужен фулфилмент? фулфилмент для маркетплейсов — хранение, сборка заказов, возвраты и учет остатков. Работаем по стандартам площадок и соблюдаем сроки поставок.
Neuro Relief USA: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
Запчасти для сельхозтехники https://selkhozdom.ru и спецтехники МТЗ, МАЗ, Амкодор — оригинальные и аналоговые детали в наличии. Двигатели, трансмиссия, гидравлика, ходовая часть с быстрой доставкой и гарантией качества.
Оформления медицинских справок https://med-official2.info справки для трудоустройства, водительские, в бассейн и учебные заведения. Купить справку онлайн быстро
Медицинская справка https://086y-spr.info 086у в Москве по доступной цене — официальное оформление для поступления в вуз или колледж.
neurontin 200: Neuro Relief USA – buying neurontin online
Медицинские справки https://norma-spravok2.info по доступной цене — официальное оформление. Быстрая запись, прозрачная стоимость и выдача документа установленного образца.
Оформление медицинских https://spr-goroda2.info справок в Москве недорого консультации специалистов и выдача официальных документов. Соблюдение стандартов и минимальные сроки получения.
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
Медицинские справки https://medit-norma1.info в Москве с прозрачной ценой — анализы и выдача официального документа без лишних ожиданий. Удобная запись, прозрачные цены и быстрое получение документа установленного образца.
Медицинская справка https://sp-dom1.ru с доставкой — официальное оформление. Удобная запись, прозрачные цены и получение документа курьером.
Получение медицинской https://gira-spravki2.ru справки с доставкой после официального оформления. Комфортная запись, минимальные сроки и законная выдача документа.
Справка 29н https://forma-029.ru в Москве с доставкой — без прохождение обязательного медосмотра в клинике. Отправка готового документа по указанному адресу.
Медицинские справки https://meduno.info и анализы в Москве — официально и удобно. Сеть из 10 клиник, оперативный прием специалистов и оформление документов по действующим стандартам.
costco online pharmacy: Smart GenRx USA – Smart GenRx USA
Iver Therapeutics: ivermectin 1% cream generic – ivermectin 3mg tablets price
neurontin 200 mg Neuro Relief USA buy neurontin 100 mg
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
Орби казино https://orby-casino.com/ онлайн-платформа с широким выбором слотов, настольных игр и бонусных предложений. Узнайте об акциях, турнирах и возможностях для комфортного игрового досуга.
Купить квартиру недорого https://spb-novostroyki-gid.ru актуальные предложения на первичном и вторичном рынке. Подбор вариантов по бюджету, помощь в ипотеке и полное юридическое сопровождение сделки.
Онлайн казино Орби orby casino com большой выбор слотов, бонусы для новых и постоянных игроков, регулярные турниры с призами.
https://sertralineusa.com/# sertraline generic
zoloft medication: zoloft generic – Sertraline USA
buy neurontin 100 mg: Neuro Relief USA – Neuro Relief USA
https://sertralineusa.shop/# buy zoloft
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# 300 mg neurontin
ivermectin rx: ivermectin buy – ivermectin 500mg
zoloft pill: sertraline generic – generic zoloft
Smart GenRx USA Smart GenRx USA best european online pharmacy
http://ivertherapeutics.com/# ivermectin cost
stromectol cvs: cost of ivermectin – Iver Therapeutics
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# medicine neurontin 300 mg
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
Iver Therapeutics: ivermectin 1mg – Iver Therapeutics
Чудові бонуси в казино — депозитні бонуси, бездепозитні бонуси та Турнір з призами. Обзори пропозицій і правила участі.
Найпопулярніша платформа казіно онлайн – популярні слоти, бонуси та турніри з призами. Огляди гри та правила участі в акціях.
Грайте в слоти онлайн — популярні ігрові автомати, джекпоти та спеціальні пропозиції. Огляди гри та можливості для комфортного харчування.
zoloft buy: zoloft cheap – generic zoloft
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft no prescription
Найкращі онлайн ігри казино – безліч ігрових автоматів, правил, бонусів покерів і. Огляди, новинки спеціальні
Квартиры в новостройках https://domik-vspb.ru от застройщика — студии, однокомнатные и семейные варианты. Сопровождение сделки и прозрачные условия покупки.
neurontin 1200 mg: Neuro Relief USA – buy neurontin 100 mg
ivermectin 5: Iver Therapeutics – ivermectin where to buy for humans
ivermectin 6 mg tablets Iver Therapeutics Iver Therapeutics
https://neuroreliefusa.com/# neurontin 800 mg price
Un’accogliente pasticceria https://www.pasticceriabonati.it con fragranti prodotti da forno, classici dolci italiani e torte natalizie personalizzate. Ingredienti naturali e attenzione a ogni dettaglio.
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# Neuro Relief USA
order neurontin over the counter: Neuro Relief USA – neurontin 600
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft tablet
zoloft buy: sertraline zoloft – generic for zoloft
Smart GenRx USA: Smart GenRx USA – online pharmacy drop shipping
https://neuroreliefusa.shop/# Neuro Relief USA
online pharmacy without insurance: Smart GenRx USA – super saver pharmacy
Smart GenRx USA pharmacy store pharmacy today
Neuro Relief USA: canada where to buy neurontin – neurontin 1200 mg
https://sertralineusa.com/# zoloft cheap
http://sertralineusa.com/# sertraline generic
canadian pharmacy online cialis: Smart GenRx USA – indian pharmacy
http://smartgenrxusa.com/# canada online pharmacy no prescription
Металлический кованый факел купить с доставкой — прочная конструкция, эстетичный внешний вид и устойчивость к погодным условиям.
online pharmacy 365: www pharmacyonline – Smart GenRx USA
https://ivertherapeutics.shop/# where to buy ivermectin pills
sertraline: buy zoloft – order zoloft
neurontin medication: Neuro Relief USA – cost of neurontin 800 mg
http://neuroreliefusa.com/# can i buy neurontin over the counter
Iver Therapeutics Iver Therapeutics Iver Therapeutics
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
Хочешь восстановить мрамор? https://conceptstone.ru устранение трещин, пятен и потертостей. Современные технологии шлифовки и кристаллизации для идеального результата.
zoloft generic: order zoloft – Sertraline USA
ivermectin gel: ivermectin lice oral – ivermectin humans
https://smartgenrxusa.com/# Smart GenRx USA
Carbon credits https://offset8capital.com and natural capital – climate projects, ESG analytics and transparent emission compensation mechanisms with long-term impact.
Свежие новости SEO https://seovestnik.ru и IT-индустрии — алгоритмы, ранжирование, веб-разработка, кибербезопасность и цифровые инструменты для бизнеса.
Строительство бетонных бассейнов под ключ https://atlapool.ru
Все самое свежее здесь: https://my-mizon.ru/best-sales/
Нужны казино бонусы? https://kazinopromokod.ru — бонусы за регистрацию и пополнение счета. Обзоры предложений и подробные правила использования кодов.
Онлайн покер покерок официальный сайт — турниры с крупными гарантиями, кеш-игры и специальные предложения для игроков. Обзоры форматов и условий участия.
Все о фундаменте https://rus-fundament.ru виды оснований, расчет нагрузки, выбор материалов и этапы строительства. Практичные советы по заливке ленточного, плитного и свайного фундамента.
Портал о жизни в ЖК https://pioneer-volgograd.ru инфраструктура, паркинг, детские площадки, охрана и сервисы. Информация для будущих и действующих жителей.
Зарубежная недвижимость https://realtyz.ru актуальные предложения в Европе, Азии и на побережье. Информация о ценах, налогах, ВНЖ и инвестиционных возможностях.
Все о ремонте квартир https://belstroyteh.ru и отделке помещений — практические инструкции, обзоры материалов и современные решения для интерьера.
Всё про строительство https://hotimsvoydom.ru и ремонт — проекты домов, фундаменты, кровля, инженерные системы и отделка. Практичные советы, инструкции и современные технологии.
Найкращі бонуси казино — депозитні акції, бездепозитні пропозиції та турніри із призами. Огляди та порівняння умов участі.
Грати в найкраще онлайн казіно — широкий вибір автоматів та настільних ігор, вітальні бонуси та спеціальні пропозиції. Дізнайтеся про умови участі та актуальні акції.
Грати в ігри слоти – великий каталог автоматів, бонуси за реєстрацію та регулярні турніри. Інформація про умови та можливості для гравців.
Онлайн ігри онлайн казино – великий вибір автоматів, рулетки та покеру з бонусами та акціями. Огляди, новинки та спеціальні пропозиції.
Онлайн покер Покер онлайн покерок — регулярные турниры, кеш-игры и специальные предложения для игроков. Обзоры возможностей платформы и условий участия.
Онлайн слот https://chickenroadgames.top/uk/ – тематичний автомат з бонусними елементами та захоплюючим процесом. Огляд гри та умови для гравців.
onlinecanadianpharmacy 24: canadian pharmacy 24h com – CertiCanPharmacy
?n yaxs? https://mineslot.club/az/ mas?n? canl? dizayn? v? ?lav? xususiyy?tl?ri olan qeyri-adi bir slot mas?n?d?r. Oyuncular ucun xususiyy?tl?r? v? s?rtl?r? n?z?r sal?n.
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
pharmacy mexico: My Mexican Pharmacy – best pharmacy in mexico
?n yaxs? https://mineslot.club/az/ mas?n? canl? dizayn? v? ?lav? xususiyy?tl?ri olan qeyri-adi bir slot mas?n?d?r. Oyuncular ucun xususiyy?tl?r? v? s?rtl?r? n?z?r sal?n.
CertiCanPharmacy: canada drugs reviews – canadian pharmacy ed medications
pet meds official website pet meds for dogs pet drugs online
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# best mail order pharmacy canada
An impressive share! I’ve just forwarded this onto a coworker who had been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast simply because I discovered it for him… lol. So allow me to reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! Life Experience Degree
canadian pharmacy prices: my canadian pharmacy – CertiCanPharmacy
http://vetfreemeds.com/# best pet rx
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
dog prescriptions online: VetFree Meds – online vet pharmacy
п»їdog medication online: pet pharmacy – pet meds official website
ойын автоматы https://minedrop.me/kk/ – т?пн?с?а т?жырымдамасы мен жар?ын дизайны бар динамикалы? ойын автоматы. Механика, бонусты? м?мкіндіктер ж?не ойын процесіні? м?мкіндіктері туралы білі?із.
My Mexican Pharmacy My Mexican Pharmacy mexico online pharmacy
https://vetfreemeds.shop/# discount pet meds
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# hydrocodone mexico pharmacy
purple pharmacy mexico: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
best pet rx: pet med – pet rx
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# pharmacy in mexico that ships to us
http://vetfreemeds.com/# pet med
Descubre https://zeusvshades250.com/es/, una tragamonedas de tematica mitologica, con bonos y funciones adicionales. Descubre la mecanica y la jugabilidad.
pet meds online: vet pharmacy – vet pharmacy online
canada drugs reviews CertiCanPharmacy canadadrugpharmacy com
certified canadian pharmacy: canadian pharmacy com – CertiCanPharmacy
http://vetfreemeds.com/# pet pharmacy
A catalog of cars https://auto.ae/catalog/ across all brands and generations—specs, engines, trim levels, and real market prices. Compare models and choose the best option.
pet pharmacy: VetFree Meds – pet meds official website
CertiCanPharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – northern pharmacy canada
http://vetfreemeds.com/# pet meds official website
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
CertiCanPharmacy canada cloud pharmacy CertiCanPharmacy
purple pharmacy online: farmacia pharmacy mexico – My Mexican Pharmacy
online pet pharmacy: pet meds online – canada pet meds
http://vetfreemeds.com/# canada pet meds
CertiCanPharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – canadapharmacyonline legit
https://certicanpharmacy.shop/# canadian pharmacy
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# mexican online pharmacies
Un sito web https://www.sopicks.it per trovare abbigliamento, accessori e prodotti alla moda con un motore di ricerca intelligente. Trova articoli per foto, marca, stile o tendenza, confronta le offerte dei negozi e crea look personalizzati in modo rapido e semplice.
Dzisiejsze mecze mecze dzis aktualny harmonogram z dokladnymi godzinami rozpoczecia. Dowiedz sie, jakie mecze pilki noznej, hokeja i koszykowki odbeda sie dzisiaj, i sledz turnieje, ligi i druzyny w jednym wygodnym kalendarzu.
Wiadomosci tenisowe https://teniswiadomosci.pl z Polski i ze swiata: najnowsze wyniki meczow, rankingi zawodniczek, analizy turniejow i wywiady z zawodniczkami. Sledz wydarzenia ATP i WTA, dowiedz sie o zwyciestwach, niespodziankach i najwazniejszych meczach sezonu.
canadian pharmacies: CertiCanPharmacy – trusted canadian pharmacy
CertiCanPharmacy: medication canadian pharmacy – canadian online drugs
https://vetfreemeds.shop/# canada pet meds
the purple pharmacy mexico My Mexican Pharmacy My Mexican Pharmacy
https://mymexicanpharmacy.shop/# My Mexican Pharmacy
Siatkowka w Polsce https://siatkowkanews.pl najnowsze wiadomosci, wyniki meczow, terminarze i transfery druzyn. Sledz PlusLige, wystepy reprezentacji narodowych i najwazniejsze wydarzenia sezonu w jednej wygodnej sekcji sportowej.
Koszykowka https://koszykowkanews.pl najnowsze wiadomosci, PLK, transfery i wyniki meczow. Sledz polska lige, turnieje miedzynarodowe i postepy zawodnikow, dowiedz sie o transferach, statystykach i najwazniejszych wydarzeniach sezonu.
Jan Blachowicz janblachowicz to polski zawodnik MMA i byly mistrz UFC w wadze polciezkiej. Pelna biografia, historia kariery, statystyki zwyciestw i porazek, najlepsze walki i aktualne wyniki.
pharmacys in mexico: purple pharmacy mexico – My Mexican Pharmacy
https://vetfreemeds.com/# dog prescriptions online
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# mexican meds
pet meds official website: pet meds official website – pet meds online
My Mexican Pharmacy: mexican medicine – pharma mexicana
https://vetfreemeds.shop/# pet drugs online
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# safe canadian pharmacy
pet prescriptions online VetFree Meds online pet pharmacy
CertiCanPharmacy: trusted canadian pharmacy – canadian drug
Julie Cash julie cash on OnlyFans features exclusive content, private posts, and regular updates for subscribers. Subscribe to gain access to original content and special offers.
vet pharmacy: pet meds online – pet drugs online
https://vetfreemeds.com/# pet meds online
IDMAN TV https://idman-tv.com.az/ live stream online: watch the channel in high quality, check today’s program guide, and find the latest TV schedule. Conveniently watch sporting events and your favorite shows live.
Free online games oyun oyna with no installation required—play instantly in your browser. A wide selection of genres: arcade, racing, strategy, puzzle, and multiplayer games are available in one click.
Everything about FC Qarabag http://www.qarabag.com.az in one place: match results and schedule, Premier League standings, squads and player stats, transfers, live streams, and home ticket sales.
Watch Selcuksport TV https://www.selcuksports.com.az live online in high quality. Check the broadcast schedule, follow sporting events, and watch matches live on a convenient platform.
Julie Cash https://juliecash.online on OnlyFans features exclusive content, private posts, and regular updates for subscribers. Subscribe to gain access to original content and special offers.
https://certicanpharmacy.shop/# CertiCanPharmacy
Exclusivo de Candy Love candylove contenido original, publicaciones vibrantes. Suscribete para ser el primero en enterarte de las nuevas publicaciones y acceder a actualizaciones privadas.
Crystal Lust crystal lust is the official website, featuring original publications, premium content, and special updates for subscribers. Stay up-to-date with new posts and gain access to exclusive content.
Brooke Tilli https://www.brooketilli.online official website features unique, intimate content, exclusive publications, and revealing updates. Access original content and the latest news on the official platform.
Shilpa Sethi shilpasethi exclusive content, breaking news, and regular updates. Get access to new publications and stay up-to-date on the most interesting events.
MiniTinah https://minitinah.es/ comparte contenido exclusivo y las ultimas noticias. Siguenos en Instagram y Twitter para enterarte antes que nadie de nuestras nuevas publicaciones y recibir actualizaciones emocionantes a diario.
CertiCanPharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – CertiCanPharmacy
Eva Elfie https://evaelfie.ing shares unique intimate content and new publications. Her official page features original materials, updates, and exclusive offers for subscribers.
Lily Phillips lily-phillips.com offers unique intimate content, exclusive publications, and revealing updates for subscribers. Stay up-to-date with new content, access to original photos, and special announcements on her official page.
Unique content from Angela White angelawhite.ing new publications, exclusive materials, and personalized updates. Stay up-to-date with new posts and access exclusive content.
Sweetie Fox sweetiefox ing offers exclusive content, original publications, and regular updates. Get access to new materials, private photos, and special announcements on the official page.
Souzan Halabi http://www.souzanhalabi.online/ shares exclusive content and new publications. Get access to private updates and original materials on the official platform.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.shop/# My Mexican Pharmacy
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
Riley Reid https://www.rileyreid.ing is a space for exclusive content, featuring candid original material and regular updates. Get access to new publications and stay up-to-date on the hottest announcements.
Shilpa Sethi shilpa sethi official page features unique, intimate content and premium publications. Private updates, fresh photos, and personal announcements are available to subscribers.
Brianna Beach’s exclusive https://briannabeach.online page features personal content, fresh posts, and the chance to stay up-to-date on new photos and videos.
Luiza Marcato Official luizamarcato exclusive updates, personal publications, and the opportunity to connect. Get access to unique content and official announcements.
Exclusive Aeries Steele https://aeriessteele.online intimate content, and original publications all in one place. New materials, special announcements, and regular updates for those who appreciate a premium format.
pharmacy mexico: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
mexico city pharmacy: order from mexico – My Mexican Pharmacy
Sabrina Cortez sabrinacortez online offers unique content and fresh publications. Join us on social media to receive exclusive updates and participate in exciting activities.
Google salaries by position https://salarydatahub.uk comparison of income, base salary, and benefits. Analysis of compensation packages and career paths at the tech company.
Exclusive content Alexis Fawx http://www.alexisfawx.online original publications and special updates. Follow us on social media to stay up-to-date on new releases and participate in exciting events.
Любишь азарт? pinap онлайн-платформа с широким выбором слотов, настольных игр и живого казино. Бонусы для новых игроков, акции, турниры и удобные способы пополнения счета доступны круглосуточно.
best pet rx pet meds for dogs best pet rx
Bunny Madison https://www.bunnymadison.online features exclusive, intimate content, and special announcements. Join us on social media to receive unique content and participate in exciting events.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.shop/# mexico city pharmacy
https://vetfreemeds.com/# pet drugs online
pet drugs online: п»їdog medication online – pet rx
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
mexican pharmacy: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
http://vetfreemeds.com/# pet meds online
Jill Kassidy Exclusives http://www.jillkassidy-official.online/ featuring original content, media updates, and special announcements.
Discover Avi Love’s https://avilove.online world: exclusive videos, photos, and premium content on OnlyFans and other platforms.
Scarlett Jones http://www.scarlettjones.in/ shares exclusive content and the latest updates. Follow her on Twitter to stay up-to-date with new publications and participate in exciting media events.
Die Welt von Monalita https://monalita.de bietet exklusive Videos, ausdrucksstarke Fotos und Premium-Inhalte auf OnlyFans und anderen beliebten Plattformen. Abonniere den Kanal, um als Erster neue Inhalte und besondere Updates zu erhalten.
Johnny Sins johnny-sins.com is the official channel for news, media updates, and exclusive content. Be the first to know about new releases and stay up-to-date on current events.
mexico pharmacy: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
Discover the world of LexiLore https://lexilore.ing exclusive videos, original photos, and vibrant content. Regular updates, new publications, and special content for subscribers.
Все самое свежее здесь: оснащение конференц залов
Serenity Cox serenitycox ing shares exclusive content and regular updates. Follow her on Instagram, Twitter, and Telegram to stay up-to-date on creative projects and inspiring events.
Dive into the world of Dolly Little dolly little original videos, exclusive photos, and unique content available on OnlyFans and other services. Regular updates and fresh publications for subscribers.
https://vetfreemeds.com/# online pet pharmacy
Купить квартиру https://sbpdomik.ru актуальные предложения на рынке недвижимости. Новостройки и вторичное жильё, удобный поиск по цене, району и площади. Подберите идеальную квартиру для жизни или инвестиций.
Karely Ruiz karelyruiz comparte contenido exclusivo y actualizaciones periodicas. Siguela en Instagram, Twitter y Telegram para estar al tanto de sus proyectos creativos y eventos inspiradores.
Discover the world of Comatozze http://www.comatozze.in/ exclusive content on OnlyFans and active updates on social media. Subscribe to stay up-to-date on new publications and exciting projects.
Get to know JakKnife https://jakknife.online and discover unique content. Regular updates, special publications, and timely announcements are available to subscribers.
The official website of MiniTina minitinah com your virtual friend with exclusive publications, personal updates, and exciting content. Follow the news and stay connected in a cozy online space.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
CertiCanPharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – CertiCanPharmacy
Нужна плитка? тротуарная плитка старый город большой ассортимент, современные формы и долговечные материалы. Подходит для мощения тротуаров, площадок и придомовых территорий.
My Mexican Pharmacy: mexican online pharmacy wegovy – mexican meds
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# adderall canadian pharmacy
At secure gaming portal you can enjoy a very immersive atmosphere with localized themes that resonate well with the Spanish audience. The bonuses are transparent and easy to track within your personal account.
https://vetfreemeds.com/# pet pharmacy
Строишь дом или забор? https://gazobeton-krasnodar.ru продажа газобетона и газоблоков в Краснодаре с доставкой по Краснодарскому краю и СКФО. В наличии автоклавные газобетонные блоки D400, D500, D600, опт и розница, расчет объема, цены от производителя, доставка на объект манипулятором
Нужен газоблок? https://gazobeton-krasnodar.ru/katalog/ каталог газоблоков и газобетона в Краснодаре: размеры, характеристики и цены на газобетонные блоки КСМК. Можно купить газоблоки с доставкой по Краснодару, краю и СКФО. Актуальная цена газоблоков, помощь в подборе, расчет объема и заказ с завода
Нужны ЖБИ? https://postroi-ka.by широкий ассортимент ЖБИ, прочные конструкции и оперативная доставка на объект. Консультации специалистов и индивидуальные условия сотрудничества.
vet pharmacy online: VetFree Meds – online vet pharmacy
Visiting verified casino website gives you access to a legitimate gaming platform with clear terms and conditions regarding bonuses. The registration is fast, and the verification process didn’t take more than a few hours in my case.
Unique content from Gattouz0Officiall – daily reviews, new materials, and the opportunity for personal interaction. Stay connected and get access to the latest publications.
Contenido exclusivo de KarelyRuiz: resenas diarias, nuevos materiales y la oportunidad de interactuar personalmente. Mantengase conectado y acceda a las ultimas publicaciones.
Discover the world of CandyLove: exclusive content, daily reviews, and direct communication. Subscribe to receive the latest updates and stay up-to-date with new publications.
Immerse yourself in the world of CrystalLust: unique content, daily reviews, and direct interaction. Here you’ll find not only content but also live, informal communication.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
Exclusive from Sky Bri – daily reviews, new publications, and direct communication. Subscribe to stay up-to-date and in the know.
mexican pharmacies that ship to us: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
official page Elle Lee features hot posts, private selfies, and real-life videos. Subscribe to receive daily updates and exclusive content.
The official LexisStar page features daily breaking news, personal selfies, and intriguing content. Subscribe to stay up-to-date with new updates.
The official delux_girlOfficiall channel features daily hot content, private selfies, and exclusive videos. Intriguing real-life moments and regular updates for those who want to get closer.
Discover the world of NaomiHughes Official: daily vibrant content, candid selfies, and dynamic videos. Real life moments and regular updates for those who appreciate a lively format.
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# tijuana pharmacy online
My Mexican Pharmacy: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
Discover the world of MickLiter: behind-the-scenes stories, bold provocations, and personal footage. All the most interesting content gathered in one place with regular updates.
intriguing publications Reislin Officiall and new materials appear regularly, creating a truly immersive experience. Personal moments, striking provocations, and unexpected materials are featured. Stay tuned for new publications.
Descubre el mundo de LiaLin Oficial: historias tras bambalinas, provocaciones audaces y videos personales. Todo el contenido mas interesante reunido en un solo lugar con actualizaciones periodicas.
Immerse yourself in the MewSlut experience: candid behind-the-scenes moments, provocative vibes, and intriguing updates all in one place.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.shop/# pharmacies in mexico
My Mexican Pharmacy: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# pharmacy mexico online
pet rx: VetFree Meds – online vet pharmacy
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
best pet rx: pet meds online – п»їdog medication online
https://mymexicanpharmacy.shop/# medicine mexico
My Mexican Pharmacy mail order pharmacy mexico My Mexican Pharmacy
http://vetfreemeds.com/# vet pharmacy online
The best of MilaSolana – sharing all the most interesting content in one channel. Behind-the-scenes atmosphere, provocative mood, and personal snippets. Stay tuned and don’t miss any new releases.
passionate atmosphere Amadani openness and a personal format of communication. Exclusive content, created without intermediaries—only for those who want more.
exclusive revelations MonalitaOfficial genuine passion and bold aesthetics. Private content you’ll find only here—directly from the author, without filters or unnecessary boundaries.
honest revelations AlinaRai Official vivid emotions and a sensual atmosphere. Unique private content, available only on this page—directly from me.
can i order online from a mexican pharmacy: My Mexican Pharmacy – My Mexican Pharmacy
bold format BigTittyGothEggOfficiall sincere emotions and expressive images. Private materials and special publications that you’ll only see here.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# mexico medicine
CertiCanPharmacy: canadian pharmacy com – CertiCanPharmacy
personal revelations EvaElfie powerful energy and private publications. Unique content, available exclusively here—directly from me.
Genuine emotions Girthmasterr bold visual presentation, and personal communication. Exclusive content revealed only to its audience.
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
mexican pharmacies that ship: farmacias online usa – phentermine in mexico pharmacy
https://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
vipps approved canadian online pharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – onlinecanadianpharmacy
Vivid revelations Sweetiefox Officiall sensual aesthetics, and a signature format. Private materials created without boundaries or templates—available only in one place.
Pure emotion ReislinOfficiall bold presentation, and a private format without boundaries. Exclusive content, personally created and available only here—for those who appreciate true energy.
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# canadian pharmacy meds
Candid style Diana Rider vibrant passion, and a unique atmosphere. Private publications and unique materials that you’ll find exclusively in this space.
Boldness and sincerity LunaOkko Officiall maximum intimacy. Personal content without intermediaries—only here and only directly from me.
dog prescriptions online: vet pharmacy online – vet pharmacy online
CertiCanPharmacy CertiCanPharmacy canadian pharmacy ltd
https://vetfreemeds.com/# pet pharmacy
A bold image LunaOkkoOfficiall strong charisma, and a personal communication format. Private publications and special materials revealed only to our audience.
Maximum candor PrincesslsiOfficiall vibrant energy, and a private atmosphere. Exclusive content is personally created and available only here—for those ready for a truly unique experience.
Frank emotions RaeLilBlac captivating aesthetics, and a personalized format. Content without unnecessary filters—directly from the author.
The energy of passion Romi Rain sincerity, and private access. Unique publications created for those who appreciate a personalized and bold format.
Играешь в казино? https://eva-vlg.ru популярная онлайн-платформа с большим выбором слотов, настольных игр и лайв-казино. Бонусы для новых игроков, регулярные акции и удобные способы пополнения доступны круглосуточно.
Нужен промокод казино? промокод на бесплатные ставки получите бесплатные вращения в популярных слотах. Актуальные бонус-коды, условия активации и пошаговая инструкция по использованию для новых и действующих игроков.
Bold aesthetics SiriDahl Officiall personal revelations, and an intimate atmosphere. Exclusive content is created without compromise—only for our audience, and only here.
Sensual style CocoLovelock Officiall vibrant energy, and an unfiltered format. Unique materials available exclusively in this space.
Лучшее казино онлайн пин ап казино рабочее зеркало слоты, джекпоты, карточные игры и лайв-трансляции. Специальные предложения для новых и постоянных пользователей, акции и турниры каждый день.
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# legal canadian pharmacy online
My Mexican Pharmacy: farmacias mexicanas – mexican rx pharm
Нужен компрессор? https://macunak.by для производства и мастерских. Надёжные системы сжатого воздуха, гарантия, монтаж и техническая поддержка на всех этапах эксплуатации.
Play unblocked games online without registration or downloading. A large catalog of games across various genres is available right in your browser at any time.
Работаешь с авито? как открыть магазин на авито профессиональное создание и оформление Авито-магазина, настройка бизнес-аккаунта и комплексное ведение. Поможем увеличить охват, повысить конверсию и масштабировать продажи.
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
Только лучшие материалы: Половой нерв: его роль в здоровье и функционировании организма
CertiCanPharmacy: canadian pharmacy service – canadian online drugs
thc vape for sale in prague thc vape for sale in prague
buy thc chocolate in prague kush for sale in prague
buy hash in prague hemp in prague
marijuana delivery in prague buy thc vape in prague
cannafood in prague cannabis store in prague
CertiCanPharmacy: canada pharmacy 24h – certified canadian international pharmacy
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# My Mexican Pharmacy
My Mexican Pharmacy pharmacys in mexico can i order online from a mexican pharmacy
canadian pharmacy 24h com: canadian drug prices – canadian pharmacy online ship to usa
mexico pharmacy: online pharmacy in mexico – My Mexican Pharmacy
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
My Mexican Pharmacy: My Mexican Pharmacy – order meds from mexico
http://mymexicanpharmacy.com/# online pharmacy
hashish shop in prague buy cannabis in prague
hemp shop in prague buy weed in telegram
buy thc vape in prague thc joint for sale in prague
hemp in prague thc chocolate shop in prague
buy weed in telegram thc joint delivery in prague
https://certicanpharmacy.com/# canadian pharmacy drugs online
thc vape for sale in prague hash for sale in prague
cannabis in prague thc chocolate in prague
buy weed in telegram marijuana in prague
cannafood for sale in prague hash for sale in prague
hashish for sale in prague kush for sale in prague
mexico pharmacy: online pharmacy mexico – medication in mexico
vet pharmacy online: VetFree Meds – dog prescriptions online
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# canadianpharmacyworld com
mexi pharmacy pharmacy delivery My Mexican Pharmacy
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# CertiCanPharmacy
buy weed in prague marijuana shop in prague
weed delivery in prague weed in prague
buy thc vape in prague marijuana in prague
cbd weed in prague weed shop in prague
Jouez-vous au casino? https://sultan-willd-fr.eu.com une plateforme de jeux moderne proposant une variete de machines a sous, de jackpots et de jeux de table. Inscription et acces faciles depuis n’importe quel appareil.
CertiCanPharmacy: CertiCanPharmacy – canadian pharmacy review
http://vetfreemeds.com/# pet pharmacy
Check this source for essential information regarding local community initiatives and the strategic goals set by leadership. The layout is very clear, which makes it easy to find specific data about upcoming public events and policy updates without much effort. It really helps bridge the gap by providing transparent and timely information that matters to every active citizen in the region.
Visit official page to find unique entertainment tips and detailed guides about the latest lifestyle trends. This platform is well-researched and provides a fresh perspective for anyone interested in high-quality content that isn’t covered by mainstream blogs. I especially like how they categorize their posts, making it easy to navigate through different themes without feeling overwhelmed.
At live casino portal you will find an extensive library of licensed slots and live dealer tables that definitely cater to all types of players. The site has a reputation for offering very competitive bonuses with fair wagering requirements, making it a solid choice for both beginners and pros. I’ve personally found their withdrawal process to be quite efficient, which is always a top priority when choosing a new platform.
Try Mr.Jackbet slots if you are looking for the official Mr.Jackbet platform with the most reliable slots and betting options. This destination is very professional and provides all the necessary details and service descriptions you might need before you start playing for real. It’s a great example of a secure environment that values transparency and makes it easy for users to find exactly what they need.
dog medicine: VetFree Meds – pet prescriptions online
http://certicanpharmacy.com/# best canadian online pharmacy
CertiCanPharmacy: best canadian pharmacy – certified canadian pharmacy
best price for viagra 100mg Sildenafil Price Guide sildenafil online
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Cheapest Sildenafil online
Inside secure India portal you will find a massive selection of games specifically tailored for the Indian market, including hits like Teen Patti and Andar Bahar. The platform utilizes high-level encryption to ensure all transactions and personal data remain secure at all times. I also found that they offer excellent local deposit options, which makes the whole experience much more convenient for users in the region.
On secure Greek portal you can enjoy a very engaging loyalty program that rewards active players with frequent cashback and exclusive tournament invitations. The platform is highly stable and performs well on both desktop and mobile browsers, ensuring you never miss a beat. It’s a great choice for those who value long-term rewards and a consistent gaming environment with plenty of variety.
At Amunra official players in the Czech region can experience high-quality slots and live dealer games in a completely secure and localized environment. The site supports popular local payment methods and offers 24/7 customer support to resolve any technical or account issues as quickly as possible. It’s a very reliable destination for those looking for a smooth registration process and a diverse library of certified casino games.
Playing https://plinko-casino-game.net/ is a fantastic way to experience this classic arcade-style game with modern graphics and certified fair mechanics. The interface is very straightforward, allowing you to jump straight into the action without dealing with overly complicated settings or menus. It’s perfect for those who enjoy quick gaming sessions where the outcome is clear and the gameplay remains consistently engaging.
Visit official Greek casino if you are looking for a premium gaming experience in Greece with a heavy focus on sports-themed slots and live betting. The site is fully localized, making navigation easy for Greek speakers, and the bonus offers are quite generous for new registrations. They have a great mix of classic casino games and modern sportsbook features that keep the overall experience very diverse.
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
Visiting biqote2024.es is essential for those tracking the latest digital trends and platform launches in Spain for the upcoming year. The site provides technical details and roadmap updates that are quite valuable for anyone involved in the local tech or gaming sectors. It serves as an official hub for news and announcements regarding several key digital initiatives starting in early 2024.
Reading fabersingt.com/buran-casino will give you a detailed overview of the platform’s features, from its unique space-themed design to its massive game library. This expert review breaks down the pros and cons, helping you decide if their current welcome package fits your playing style. It’s a very helpful resource for anyone who likes to do a bit of research before committing to a new online casino.
Visiting top Mexico athlete gives you a detailed look into the career and professional achievements of one of Mexico’s top football stars. The site includes exclusive content, career milestones, and regular updates that are perfect for dedicated fans of the midfielder. It’s a well-organized tribute to his journey from local clubs to the international stage and his ongoing impact on the sport.
pharmacy home delivery: indian pharmacy – US Pharma Index
On official news portal you will find a wide range of articles covering everything from local football to international sports tournaments. It’s a comprehensive portal for anyone who wants to stay updated on Mexican sports without having to visit multiple different news sites. The quality of the reporting is very high, and they cover a diverse range of athletic disciplines beyond just soccer.
Explore top predictions portal to find professional analysis and data-driven predictions for all major sporting events in the region. The site uses advanced statistical models to help users make more informed decisions when placing their bets on football, baseball, or other popular sports. It’s a great starting point for anyone looking to add a layer of expert insight to their wagering strategy.
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# Ivermectin Access USA
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Cheap generic Viagra
This official club portal portal provides comprehensive coverage of the club’s history, current roster, and community initiatives in the Monterrey region. I check it regularly for official injury reports and transfer news to stay updated on the team’s latest developments. It’s a great resource for dedicated supporters who want to follow every aspect of the club’s journey in the league.
See El Toluca link for the most accurate statistics and official statements directly from the club’s management this season. The site offers a detailed look at the team’s performance metrics and upcoming match analysis, which is perfect for fans who like to dive deep into the numbers. It’s a professional and well-maintained site that serves as the official voice of the team for its loyal fanbase.
Checking https://chivas-de-guadalajara.com.mx/ is a must for any fan looking for the latest news, match schedules, and official team updates. The portal provides in-depth coverage of the club’s performance and includes exclusive interviews with players and coaching staff throughout the season. It’s the most reliable source for verified information regarding upcoming fixtures and official club announcements.
Using official 365bet sports allows you to place bets on all major Mexican and international leagues with very competitive odds and live updates. The platform is designed for both pre-match and in-play wagering, making it a versatile tool for sports fans who like to stay in the action. I find their interface very clean, which helps a lot when you need to make quick decisions during a live match.
Using legal betting Mexico ensures that you are only accessing verified and licensed operators that fully comply with local Mexican laws. This guide is essential for players who prioritize financial security and want to avoid offshore sites with questionable reputations. It provides a clear list of legal platforms and explains the current regulations in a way that is very easy to understand.
buy Viagra online: cheap viagra – Viagra online price
http://uspharmaindex.com/# canadian pharmacy tampa
ivermectin humans ivermectin over the counter ivermectin cost canada
Sildenafil Citrate Tablets 100mg: viagra without prescription – viagra without prescription
https://uspharmaindex.com/# US Pharma Index
секс порно шлюхи ульяновск
купить героин в шарье мефедрон телеграмм купить
работа грузчиком грузчики недорого
работа грузчик оплатой грузчики мебели недорого
Generic Viagra for sale: Sildenafil Price Guide – order viagra
Медицинская мебель https://tenchat.ru/0614265/ это основа оснащения клиник, лабораторий и частных кабинетов. Мы предлагаем мебель медицинская для любых задач: шкафы, столы, тумбы, стеллажи и специализированные решения. В ассортименте можно купить медецинскую мебель, соответствующая санитарным требованиям и стандартам безопасности.
Play online https://bloxd-io.com.az for free right in your browser. Build, compete, and explore the world in dynamic multiplayer mode with no downloads or installations required.
Football online http://www.qol.com.az goals, live match results, top scorers table, and detailed statistics. Follow the news and never miss the action.
pin up казино официальный сайт https://games-pinup.ru
El sitio web oficial de Kareli Ruiz https://www.karelyruiz.es ofrece contenido exclusivo, noticias de ultima hora y actualizaciones periodicas. Mantengase al dia con las nuevas publicaciones y anuncios.
Lily Phillips https://www.lilyphillips.es te invita a un mundo de creatividad, conexion y emocionantes descubrimientos. Siguela en Instagram y Twitter para estar al tanto de nuevas publicaciones y proyectos inspiradores.
http://uspharmaindex.com/# prices pharmacy
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# Ivermectin Access USA
buy viagra here: Viagra generic over the counter – Viagra online price
canada pharmacy not requiring prescription: canadian discount pharmacy – US Pharma Index
Ivermectin Access USA ivermectin 4 tablets price ivermectin 12
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# viagra without prescription
http://uspharmaindex.com/# canadian pharmacy meds reviews
Ivermectin Access USA: Ivermectin Access USA – stromectol usa
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Sildenafil 100mg price
pharmacy express: US Pharma Index – US Pharma Index
ivermectin tablets order: ivermectin 4000 mcg – Ivermectin Access USA
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Buy Viagra online cheap
US Pharma Index canadian pharmacies not requiring prescription US Pharma Index
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Viagra online price
Ivermectin Access USA: generic ivermectin cream – Ivermectin Access USA
reliable canadian pharmacy reviews: legitimate online pharmacy uk – reputable overseas online pharmacies
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
Order Viagra 50 mg online: Sildenafil Price Guide – Buy Viagra online cheap
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Cheapest Sildenafil online
buy Viagra online: Viagra generic over the counter – generic sildenafil
https://uspharmaindex.com/# pharmacy discount coupons
Нужны столбики? мобильный столбик столбики для складов, парковок и общественных пространств. Прочные материалы, устойчивое основание и удобство перемещения обеспечивают безопасность и порядок.
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# stromectol 3mg tablets
Looking for a yacht? exclusive boat charters in Cyprus for unforgettable sea adventures. Charter luxury yachts, catamarans, or motorboats with or without crew. Explore crystal-clear waters, secluded bays, and iconic coastal locations in first-class comfort onboard.
где можно купить провода купить электрику в минске
Ivermectin Access USA: ivermectin usa – stromectol 3 mg price
safe online pharmacies in canada: canadian pharmacy meds review – US Pharma Index
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Sildenafil Citrate Tablets 100mg
online pharmacy quick delivery best mail order pharmacy canada pharmacies in canada that ship to the us
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Generic Viagra online
online pharmacy ed: US Pharma Index – US Pharma Index
https://uspharmaindex.shop/# US Pharma Index
US Pharma Index: my canadian pharmacy reviews – best online pharmacy india
https://uspharmaindex.com/# US Pharma Index
US Pharma Index: top 10 online pharmacy in india – US Pharma Index
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# Ivermectin Access USA
generic sildenafil Sildenafil Price Guide Viagra online price
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Generic Viagra online
Sildenafil 100mg price: Sildenafil Price Guide – sildenafil over the counter
US Pharma Index: US Pharma Index – pharmacy discount card
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Cheap generic Viagra
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Viagra generic over the counter
US Pharma Index: US Pharma Index – US Pharma Index
https://uspharmaindex.com/# pharmacy rx world canada
Cheapest Sildenafil online: Sildenafil Price Guide – Cheap generic Viagra
canadian pharmacy review: usa pharmacy – canadian pharmacy meds reviews
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# ivermectin tablets
US Pharma Index US Pharma Index US Pharma Index
http://uspharmaindex.com/# canadian pharmacy coupon
order viagra: Sildenafil Price Guide – Cheap generic Viagra
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# ivermectin buy australia
Cheapest Sildenafil online: Sildenafil 100mg price – buy viagra here
US Pharma Index: no rx pharmacy – US Pharma Index
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Cheap generic Viagra online
http://uspharmaindex.com/# US Pharma Index
п»їorder stromectol online buy stromectol Ivermectin Access USA
buy ivermectin pills: stromectol coronavirus – ivermectin 3
Viagra generic over the counter: Sildenafil Price Guide – Cheap Viagra 100mg
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Buy generic 100mg Viagra online
Ivermectin Access USA: stromectol price in india – Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
Ivermectin Access USA: Ivermectin Access USA – ivermectin new zealand
ivermectin otc: ivermectin 3 mg tabs – Ivermectin Access USA
https://uspharmaindex.shop/# canada drugstore pharmacy rx
Ivermectin Access USA where to buy ivermectin Ivermectin Access USA
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Viagra without a doctor prescription Canada
US Pharma Index: affordable pharmacy – cheap pharmacy no prescription
Sildenafil 100mg price: Cheap Sildenafil 100mg – Sildenafil Citrate Tablets 100mg
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# viagra without prescription
ivermectin lice: Ivermectin Access USA – Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
ivermectin: Ivermectin Access USA – how much is ivermectin
US Pharma Index: cheap online pharmacy – my canadian pharmacy
viagra canada best price for viagra 100mg cheap viagra
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# price of ivermectin
http://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
stromectol 3mg cost: ivermectin 80 mg – Ivermectin Access USA
https://uspharmaindex.com/# pharmacy shop
US Pharma Index: US Pharma Index – legitimate mexican pharmacy online
Нужны столбики? переносные ограждения столбика столбики для складов, парковок и общественных пространств. Прочные материалы, устойчивое основание и удобство перемещения обеспечивают безопасность и порядок.
купить кабель м кабель электрический купить минск
Ivermectin Access USA: stromectol covid – stromectol pill
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# ivermectin 2ml
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# best price for viagra 100mg
Ivermectin Access USA stromectol pills ivermectin ebay
Buy Viagra online cheap: Sildenafil Price Guide – Viagra online price
http://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# over the counter sildenafil
stromectol 3mg: stromectol cream – Ivermectin Access USA
https://uspharmaindex.com/# cheap scripts pharmacy
US Pharma Index: US Pharma Index – US Pharma Index
http://uspharmaindex.com/# usa pharmacy
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Cheap Sildenafil 100mg
Viagra online price: Sildenafil Price Guide – buy viagra here
Ivermectin Access USA: ivermectin oral 0 8 – ivermectin iv
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# Ivermectin Access USA
Cheap Viagra 100mg Buy generic 100mg Viagra online Order Viagra 50 mg online
http://uspharmaindex.com/# med pharmacy
best price for viagra 100mg: best price for viagra 100mg – Sildenafil Citrate Tablets 100mg
Ivermectin Access USA: Ivermectin Access USA – Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# ivermectin 8000
https://uspharmaindex.com/# US Pharma Index
Viagra tablet online: Viagra tablet online – Cheap Viagra 100mg
http://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
http://uspharmaindex.com/# US Pharma Index
over the counter sildenafil: Sildenafil Price Guide – sildenafil over the counter
buy viagra here: Viagra tablet online – Sildenafil Citrate Tablets 100mg
Ivermectin Access USA stromectol prices Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# stromectol prices
ivermectin cost uk: Ivermectin Access USA – Ivermectin Access USA
US Pharma Index: US Pharma Index – canadian pharmacy victoza
us pharmacy: vipps canadian pharmacy – your pharmacy online
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Sildenafil 100mg price
US Pharma Index: buying drugs from canada – US Pharma Index
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# cheapest viagra
US Pharma Index canadadrugpharmacy com legit online pharmacy
https://uspharmaindex.com/# canadian compounding pharmacy
which online pharmacy is reliable: online pharmacy in turkey – US Pharma Index
Cheap Sildenafil 100mg: Sildenafil 100mg price – Order Viagra 50 mg online
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# cheapest viagra
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# ivermectin
Ivermectin Access USA: where to buy stromectol – ivermectin 3mg tablets price
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# cheapest viagra
buy stromectol online: ivermectin lotion – Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# stromectol tab 3mg
Ivermectin Access USA ivermectin cost ivermectin uk coronavirus
ivermectin for sale: Ivermectin Access USA – Ivermectin Access USA
http://uspharmaindex.com/# bitcoin pharmacy online
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# stromectol oral
Ivermectin Access USA: stromectol 3mg tablets – stromectol online
Ivermectin Access USA: ivermectin 8 mg – Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.shop/# Ivermectin Access USA
https://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# ivermectin price canada
my canadian pharmacy rx: canadian pharmacy without prescription – your pharmacy online
https://sildenafilpriceguide.shop/# Cheap generic Viagra
What is the name of the Mario game https://super-mario-play.com
Viagra online price: buy viagra here – Cheap generic Viagra online
US Pharma Index best online pharmacy for viagra online pharmacy prescription
http://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# ivermectin 3 mg tabs
ivermectin 3mg: Ivermectin Access USA – Ivermectin Access USA
buy Viagra over the counter: Sildenafil Price Guide – Viagra without a doctor prescription Canada
ремонт квартири 1 кв м ремонт квартир вторинка
https://uspharmaindex.shop/# online pharmacy ed
stromectol tablet 3 mg: Ivermectin Access USA – Ivermectin Access USA
http://ivermectinaccessusa.com/# Ivermectin Access USA
US Pharma Index: US Pharma Index – trust pharmacy
https://sildenafilpriceguide.com/# Generic Viagra for sale
ivermectin 3 mg Ivermectin Access USA ivermectin 500ml